Figure 7.
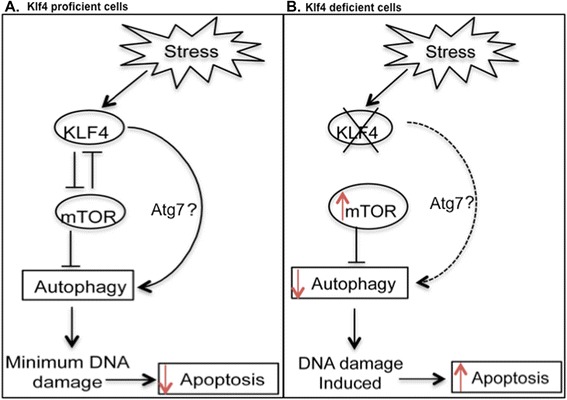
Diagraphic illustration of involvement of Klf4 in autophagy to prevent DNA damage induced apoptosis. This illustration outlines the regulation of autophagy in Klf4 proficient and deficient cells during stress and places our results in the context of known and potential relationships between KLF4, mTOR, autophagy, DNA damage and apoptosis. Based on the present study and as previously shown in [35], in wild-type MEFs, KLF4 is induced under stress and might induce autophagy in mTOR dependent or independent manners. Autophagy then removes damaged cellular components and prevents DNA damage as well as apoptosis (A). On the other hand, in MEFs lacking Klf4, autophagy induction is impaired due to mTOR hyperactivity and other unknown mechanisms. As a result, under starvation stress impaired autophagy promotes DNA damage and leads to increased apoptosis (B). KLF4 might induce autophagy by negatively regulating mTOR. However, KLF4 may also regulate autophagy in an mTOR-independent mechanism, possibly involving regulations of autophagy-related genes such as Atg7.
