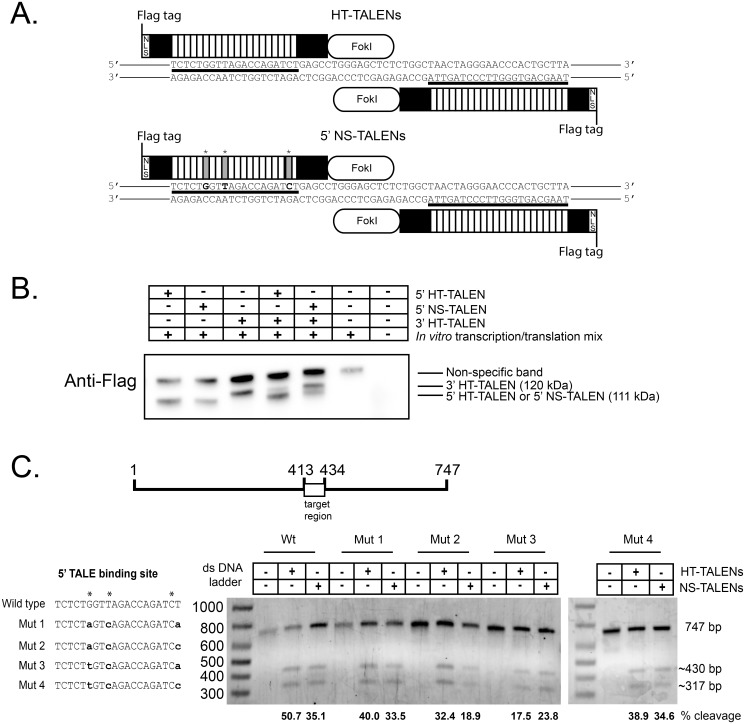
Fig 2. HT-TALENs and NS-TALENs cleave an HIV-1 DNA fragment in vitro.
A. Schematic diagram representing HT-TALENs and NS-TALENs bound to their cognate DNA target sequence (thick lines). Relative locations of the Fok1 endonuclease, Flag epitope tag, and nuclear localization sequence (NLS) are indicated. Asterisks and grey boxes designate where a “NS” coding TALE repeat was used in the 5’ NS-TALEN construction. B. Western blot of in vitro transcription/translation reactions containing no expression plasmids, each TALEN alone, the HT-TALEN pair, or the NS-TALEN pair. C. Gel electrophoresis analysis of in vitro cleavage reactions containing no TALEN plasmids, the HT-TALEN pair, or the NS-TALEN pair. The HIV-1 target DNA fragment size is 747 bp, with expected on-target cleavage products of approximately 430 bp and 317 bp. Quantification of cleavage was performed using ImageJ software and is shown below the gel image. D. The HIV-1 target DNA fragment from (C) was mutated in the 5’ TALE binding site to create a set of triple mutant templates (Mut1-Mut4). The sequences of Mut1-Mut4 are depicted in bold, lowercase font and mutated positions are indicated by asterisks. Cleavage reactions containing either the HT-TALEN or NS-TALEN pairs incubated with the HIV-1 target templates were size fractionated by electrophoresis and quantified by densitometry with ImageJ [39].