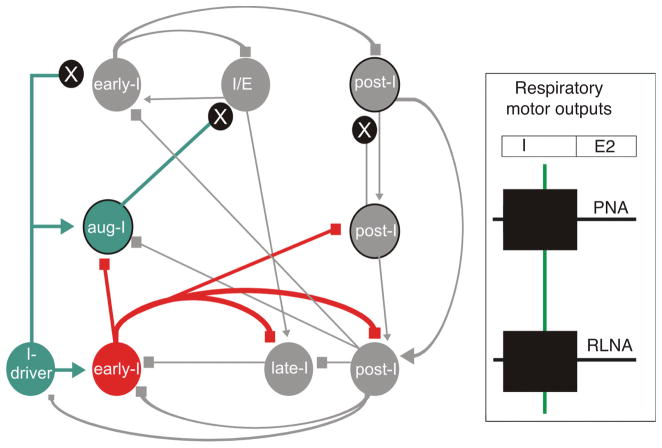
Figure 6.
Illustration of the effect of postsynaptic blockade of glutamatergic neurotransmission (e.g., NMDA-receptor antagonism) within the dorsolateral pons. Local blockade of excitatory synaptic interaction (black circles with white “x”) in the pons suppresses the efference copies 1–2 (see text and Fig. 5) causing blockade of the descending excitatory synaptic input from the pontine I/E neurons to the medullary late-I population. This abolishes the pontine mediated timing of the inspiratory/expiratory phase transition causing arrest in the inspiratory phase (apneusis). Figure adapted, with permission, from Mörschel and Dutschmann, 2009.