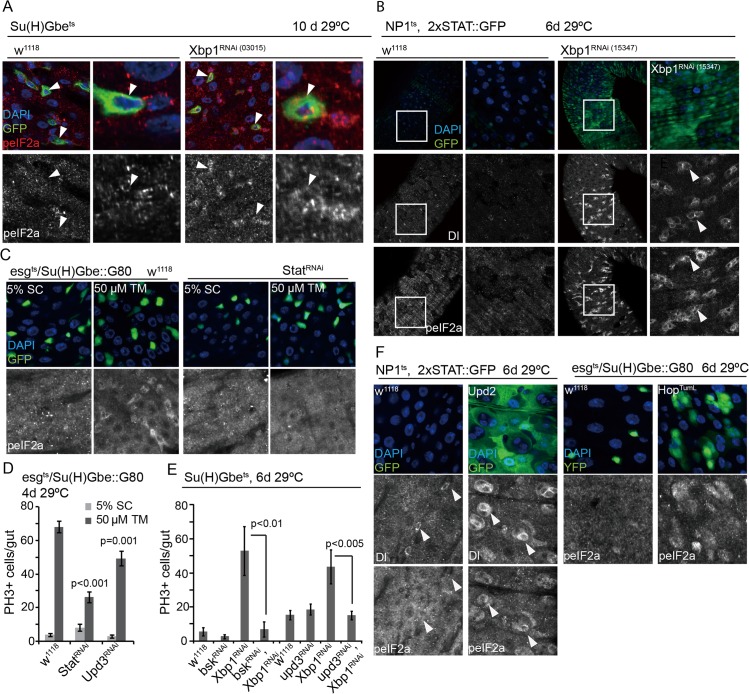
Fig 4. Non-autonomous activation of PERK in ISCs by JAK/Stat signaling.
(A) Loss of Xbp1 (Xbp1RNAi: HMS03015) specifically in EBs (using Su(H)Gbe::Gal4,tubG80ts) increases the phosphorylation of eIF2α in ISCs/EBs. DAPI, blue; GFP, green, peIF2α red; peIF2α shown as separate channel in white. Arrowheads for orientation. (B) Increased phosphorylation of eIF2α in ISCs/EBs and activation of JAK/Stat signaling in the gut of flies in which Xbp1 is knocked down in ECs. 2XSTAT::GFP was used as a reporter for Stat activity. (DAPI, blue; GFP, green; Dl and peIF2α shown as separate channels in white). (C) Knockdown of Stat in ISCs (esgts,Su(H)Gbe::G80) inhibits eIF2α phosphorylation in ISCs under ER stress. Intestines were exposed to either mock conditions (5% sucrose) or to 50 μM tunicamycin (TM). DAPI, blue; YFP, green, peIF2α shown as separate channel in white. Arrowheads for orientation. (D) Knockdown of Stat or Upd3 in ISCs prevents tunicamycin-induced ISC proliferation. Averages and SEM are shown. P values from Student’s T test, N>10. (E) Knockdown of JNK (BskRNAi) or Upd (Upd3RNAi) inhibits ISC over-proliferation induced by loss of Xbp1 in EBs (using Su(H)Gbe::Gal4,tubG80ts). Averages and SEM are shown. P values from Student’s T test, N>10. (F) Activation of JAK/Stat pathway either Upd2 overexpression in ECs (using NP1ts) or specifically in ISCs by over-exression of Hoptuml (using esgts/Su(H)Gbe::G80) promotes the phosphorylation of eIF2α in ISCs. DAPI, blue; GFP, green peIF2α and Dl shown as separate channel in white. See also S2, S4 and S5 Figs.