Fig 5. In vivo imaging assay showing the intestinal alkaline phosphatase-induced reduction in bacterial translocation.
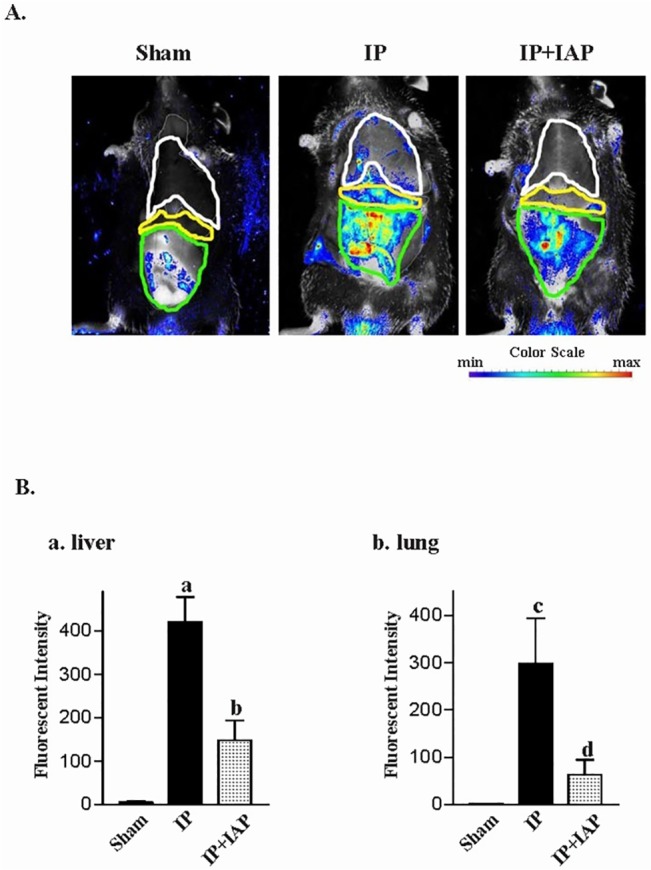
A: At 24 h after the induction of peritonitis, mice were subjected to in vivo imaging, and red fluorescence was recorded. B: The fluorescence intensities in each organ area. (a) Fluorescence intensity in the liver, (b) fluorescence intensity in the lungs; a/c P < 0.05 vs. sham, b/d P < 0.05 vs. IP. The experiments were repeated in at least three individuals. IP: Injective peritonitis; IAP: intestinal alkaline phosphatase.
