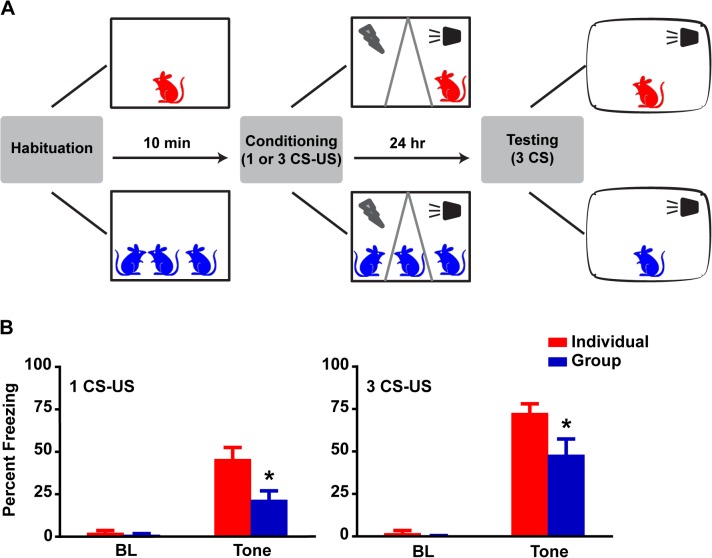
Fig 1. Group conditioning causes a robust reduction in subsequent fear expression.
(A) Schematic: rats are divided between Individual and Group conditions. After a 10-min period, a transparent insert is placed and rats are assigned to 1 of 3 compartments. A single or three tones (CS) co-terminating with a footshock (US) are delivered. Twenty-four hours later, the rats are exposed to three CS presentations in a different context for LTM testing. (B) Group rats freeze significantly less than Individuals during CS presentation while maintaining similar low levels of Pre-CS baseline (BL) freezing. Two-way Repeated Measures (RM) ANOVA revealed an effect of condition (Individual or Group), F (1, 34) = 8.93, p<0.01, and an interaction (BL x CS [average of 3]), F (1, 34) = 6.12, p<0.05. Post-hoc tests revealed no differences for BL, p>0.1, and a robust reduction in Group CS freezing, p<0.001. This was replicated in a LTM test for 3 CS-US deliveries during conditioning. Two-way RM ANOVA revealed an effect of condition, F (1, 31) = 5.05, p<0.05, and an interaction, F (1, 31) = 4.17, p<0.05. Post-hoc tests revealed no differences for BL, p>0.1, and a significant reduction in Group CS freezing, p<0.01. Data presented as mean + sem.