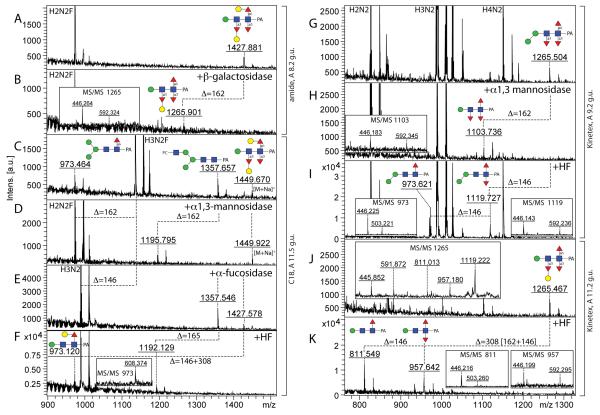
Figure 6. Chemical and enzymatic treatments of pyridylamino-labelled trifucosylated N-glycans.
Selected fractions (either RP-amide, C18 or Kinetex) of trifucosylated N-glycans were analysed by MALDI-TOF MS with the same m/z 1427 glycan being found in both the amide 8.2 g.u and C18 11.5 g.u. fractions (A,C; see MS/MS in Figure 4I), whereas two isomers with m/z 1265 were detected in two different Kinetex fractions (9.2 and 11.2 g.u.; G and J; MS/MS respectively in Figure 4H or inset in panel J). The fractions were treated with Aspergillus β1,4-specific galactosidase (B), Xanthomonas α1,2/3-mannosidase (D,H), bovine α-fucosidase (E), hydrofluoric acid (I,K) or hydrofluoric acid after α-fucosidase (F). Major glycan species in the relevant fractions are ‘off-scale’ in order to highlight the low-intensity, but complex structures. Losses of 146, 162 and 165 (i.e., of fucose, hexose and phosphorylcholine) are indicated and most m/z values are for [M+H]+ ions. Insets show regions of relevant MS/MS spectra for digestion products.