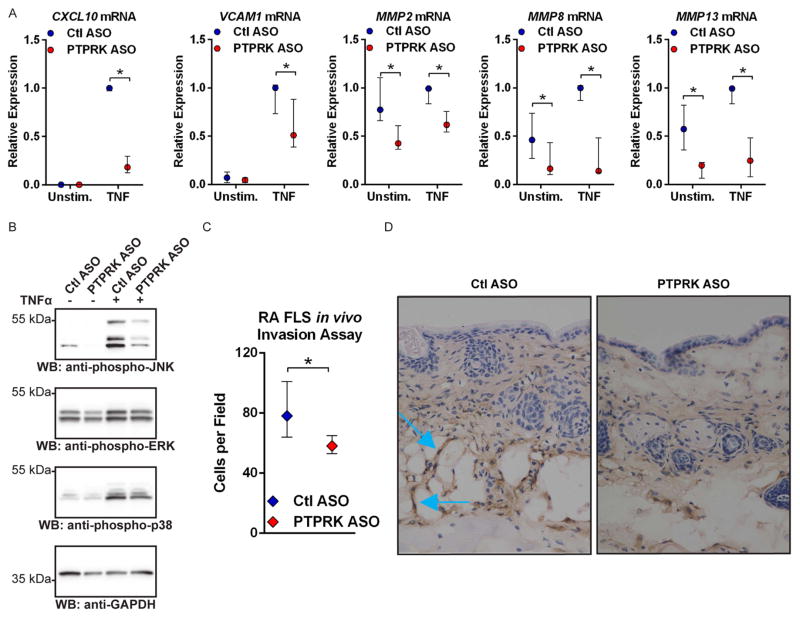
Figure 4.
RPTPκ is required for the pathogenic action of RA FLS. (A) ASO-treated RA FLS were stimulated with 50 ng/mL TNFα for 24 h or left unstimulated. Graph shows median±IQR mRNA expression levels relative to the Ctl ASO-treated, TNFα-stimulated samples from the same FLS line. Data from four (MMP8 and MMP13) or five (CXCL10, VCAM1, MMP2) independent experiments in different FLS lines are shown. *p<0.05, Mann–Whitney test. (B) Western blotting of lysates from ASO-treated RA FLS stimulated with 50 ng/mL TNFα for 15 min or left unstimulated. Data are representative of four independent experiments in different FLS lines. (C and D) ASO-treated RA FLS were intradermally implanted into nude mice following subcutaneous injection of CFA. After 5 days, FLS invasion towards the inflammation site was measured by immunohistochemical staining of FLS in skin immediately adjacent the CFA injection site with an anti-human class I HLA antibody. (C) Graph shows median±IQR cells per field. Data from three independent experiments in different FLS lines are shown. *p<0.05, Wilcoxon-matched pairs signed-rank test. (D) Representative 40× images of mouse skin samples. Blue arrows indicate invading FLS, identified by anti-human class I HLA antibody positivity.
RPTPκ, receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase κ; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; FLS, fibroblast-like synoviocytes; ASO, antisense oligonucleotide; GADPH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; CFA, complete Freunds adjuvant; HLA, human leucocyte antigen; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinases; WB, Western blotting.