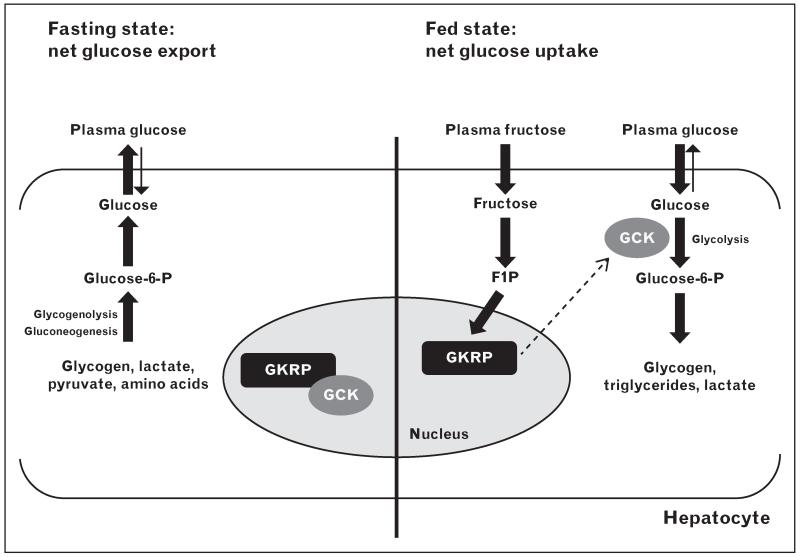
FIGURE 1.
Model of GKRP regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism. In the fasting state (left), GCK is inhibited by GKRP and sequestered in the nucleus. The hepatocyte is active in producing glucose via glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, and exports glucose to the circulation for use by peripheral tissues. In the fed state (right), GCK is released from GKRP inhibition by glucose (binding to GCK) and F1P (binding to GKRP). Glucose phosphorylation leads to enhanced glycolytic flux and glucose disposal and storage. F1P, fructose 1-phosphate; GCK, glucokinase; GKRP, glucokinase regulatory protein.