Figure 2.
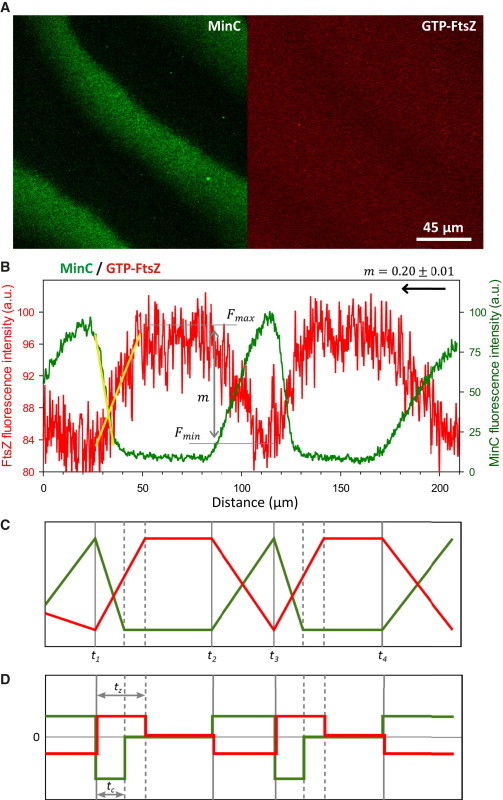
Dynamic coupling of MinCDE and FtsZ propagating waves on ZipA-SLBs. (A) Confocal fluorescence micrographs showing MinCDE (labeled protein: eGFP-MinC) and FtsZ (labeled protein: FtsZ-Alexa647) waves observed upon joint reconstruction on ZipA-SLBs. (B) Fluorescence intensity profiles of MinC and FtsZ acquired from the image shown in A. MinC displaces FtsZ in such a way that the maximal intensity of FtsZ coincides with the minimal signal of MinC. Whereas MinC has a sharp concentration maximum toward the rear of the wave, the maximum of FtsZ is relatively broad. The FtsZ wave observed in these conditions was characterized by a modulation value, m, of 0.20 ± 0.01. The arrow indicates the direction of the propagating wave. The slopes of the FtsZ and MinC profiles are highlighted with yellow lines. The wavelength of this wave is 95 μm, the period is 130 s, and the velocity is 0.73 μm/s. (C) Scheme of the MinC and FtsZ profiles. FtsZ reacts almost immediately to the decrease (times t1 and t3) and increase (times t2 and t4) of MinC concentration on the membrane. (D) Scheme of the derivatives of the MinC and FtsZ profiles. The response of FtsZ to MinC during the membrane attachment phase is somewhat slower than that observed during detachment: MinC reaches its steady state after time tc after the time point t1, whereas FtsZ requires a longer time tz. To see this figure in color, go online.
