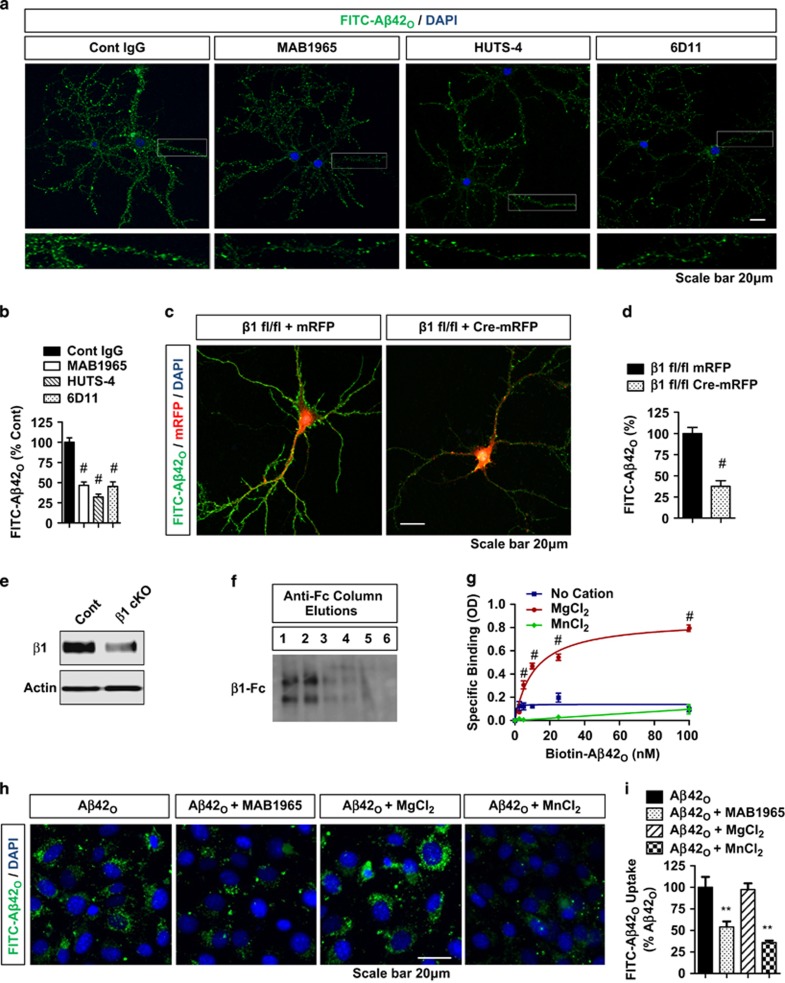
Figure 2.
β1-Integrin allosteric modulation or activation reduces Aβ42O binding to neurons, HT22 cells, and purified β1-integrin as effectively as the loss of β1-integrin (a and b) FITC-Aβ42O (100 nM, 1 h) binding to DIV21 primary hippocampal neurons with/without prior treatment (1 h) of control IgG, MAB1965 (β1-integrin allosteric modulator, 1 : 250), HUTS-4 (β1-integrin allosteric activator, 1 : 250), and/or 6D11 (PrPc blocking, 1 : 50) monoclonal antibodies. Bottom panel magnified from regions of white rectangles. (b) Quantification of FITC-Aβ42O binding (n⩾5 replicates, ANOVA, post hoc Tukey, #P<0.0005 compared with control IgG). Error bars represent S.E.M. (c–e) FITC-Aβ42O (100 nM, 1 h) binding to β1-integrin fl/fl neurons transduced with Lenti-mRFP (cont) or Lenti-Cre-mRFP (β1 cKO). (d) Quantification of FITC-Aβ42O binding (n=5 replicates, T-test, #P<0.0005). (e) Representative blots of β1-integrin from cKO (Lenti-Cre-mRFP) versus cont (Lenti-mRFP) neurons (all neurons including nontransduced). (f) Conditioned medium from CHO cells transfected with β1-integrin-Fc affinity purified with anti-Fc affinity column, sequentially eluted, and immunoblotted with anti-Fc. (g) Purified β1-integrin-Fc from fractions 1 and 2 captured by 96-well plates coated with anti-Fc IgG, subjected to biotin-Aβ42O binding and/or incubated with different cations (MgCl2, 5 mM and MnCl2, 0.5 mM). (h) Kd=10.3 nM with MgCl2. Two-way ANOVA post hoc Bonferroni, n=4 replicates, #P<0.0005. (h and i) HT22 cells treated with FITC-Aβ42O (0.1 μM, 2 h) and/or β1-integrin blocking IgG (MAB1965, 1 : 500), MnCl2 (0.5 mM), or MgCl2 (5 mM), and subjected fluorescence microscopy. (h) Representative images of FITC-Aβ42O binding/uptake show inhibition by MAB1965 antibody and MnCl2. (i) Quantification of mean intensities of FITC-Aβ42O binding/uptake (n=4 replicates, ANOVA, post hoc Tukey, **P<0.005 compared with FITC-Aβ42O alone)