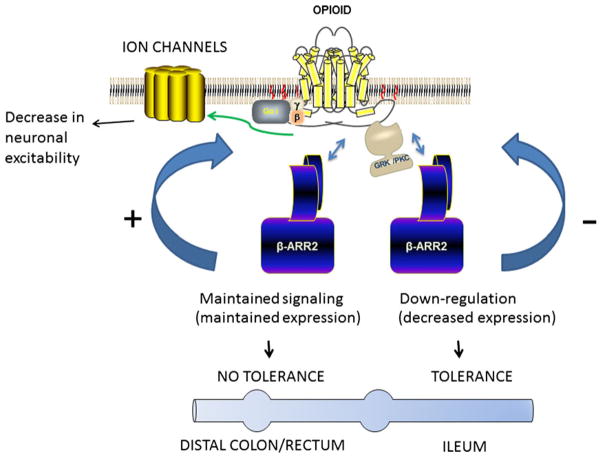
Figure 1.
General scheme of the role of β-arrestin2 in the tolerance to morphine in the ileum and colon. Agonist binding to the μ-opioid receptor activates G-protein signaling, and phosphorylation of the receptor by G-protein receptor kinase or protein kinase C dependent on the specific agonist. Phosphorylation leads to recruitment of β-arrestin2. In the ileum, repeated administration of morphine results in down-regulation of β-arrestin2 levels and development of tolerance. In the colon, repeated morphine administration does not affect β-arrestin2 levels and tolerance does not develop. Tolerance in the colon develops in the β-arrestin2 knockout mouse.