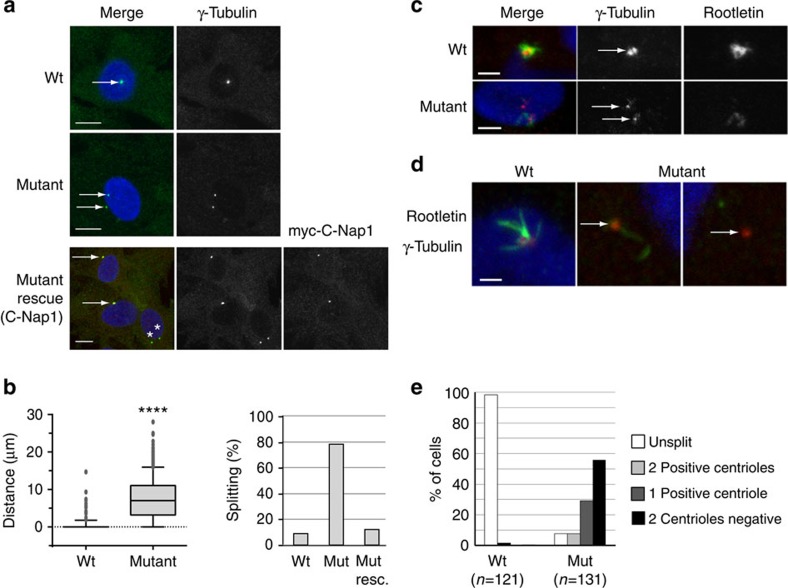
Figure 3. Centrosome splitting and rootletin loss in SHGC mutant cells.
(a) Centrosomes were visualized (arrows) with gamma-tubulin immunolabelling (green) on individual fibroblasts from wild-type and SHGC mutant animals. Centrosome splitting in mutant cells was rescued by transient expression of myc-tagged human C-Nap1. Myc labelling (red) revealed unsplit centrosomes (white arrows) in 88% of the cells (n=42) as opposed to 21% in nontransfected cells (**, n=230). DNA was stained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) Box and whiskers diagram: distance between two centrosomes measured on Z projections from different fields (SP5 Leica), for 344 wild-type and 686 SHGC mutant cells during exponential growth. The mean distance equals 0 for wild-type cells and 7.48 μm for SHGC mutant cells. The mean, upper and lower decile, upper and lower quartile and interquartile range of data (individual dots: outliers). Student's t-test following two-tailed analysis of variance (****P<0.0001). Histogram: percentage of cells with split centrosomes in 344 wild-type and 686 SHGC mutant cells, and following rescue with human C-Nap1. (c) Centrosome splitting and reduction in rootletin levels in the SHGC mutant kidney. Centrosomes (arrows) were visualized by immunolabelling with gamma-tubulin (red) and the intercentriolar protein linker rootletin (green). DNA was stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. (d) Severe reduction of Rootletin on the centrosome of SHGC mutant fibroblasts. Wild-type cells (left panel) present a strong rootletin staining (green) in between both centrioles (gamma-tubulin in red) and extending outside the intercentriolar region. Mutant fibroblasts show either severely reduced (mid panel) or undetectable (right panel) levels of rootletin (arrows). The two latter images are from the same cell. DNA was stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 2 μm. (e) Quantification of rootletin staining in wild-type and mutant fibroblasts. Centrosome splitting was scored together with the presence of rootletin near the unsplit centrosome (white bar) or in any or none of the two split centrioles (grey and dark bars). Rootletin was tightly associated with the unsplit centrosome (95% of the cases) in wild-type fibroblasts as opposed to less than 10% in mutant cells. More than 50% mutant cells exhibited a split centrosome with no detectable rootletin.