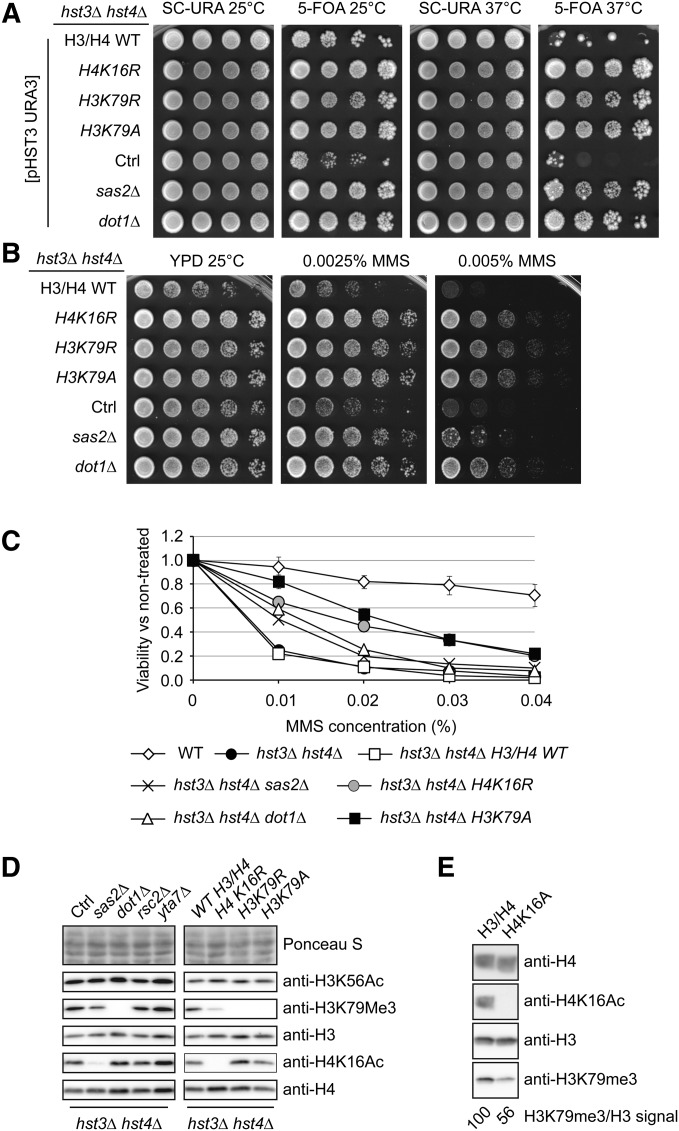
Figure 4.
Mutations that prevent modifications of H3 lysine 79 or H4 lysine 16 suppress the MMS sensitivity and Ts- phenotypes of hst3∆ hst4∆ mutants. (A) Mutations of enzymes that methylate H3K79 or acetylate H4K16, or point mutations of these residues, suppress the Ts- phenotype of hst3∆ hst4∆ mutants. Fivefold serial dilutions of cells carrying a centromeric plasmid expressing URA3 and HST3 were spotted on the indicated medium and grown at either 25 or 37°. (B and C) The sensitivity of hst3Δ hst4Δ mutants to MMS is rescued by mutations that reduce H3K79 methylation or H4K16Ac. (B) Fivefold serial dilutions of cells were spotted onto YPD medium containing MMS and incubated at 25°. (C) Exponentially growing cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of MMS for 90 min at 25°. Viability was defined as the ratio of the number of colonies that arose after MMS treatment to the number colonies formed by cells that were not exposed to MMS. Error bars, standard error of the mean from at least three independent experiments for each strain. (D and E) Whole-cell lysates of exponentially growing cells were probed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies (see Figure S1 for densitometry analysis). Ctrl, hst3∆ hst4∆ cells.