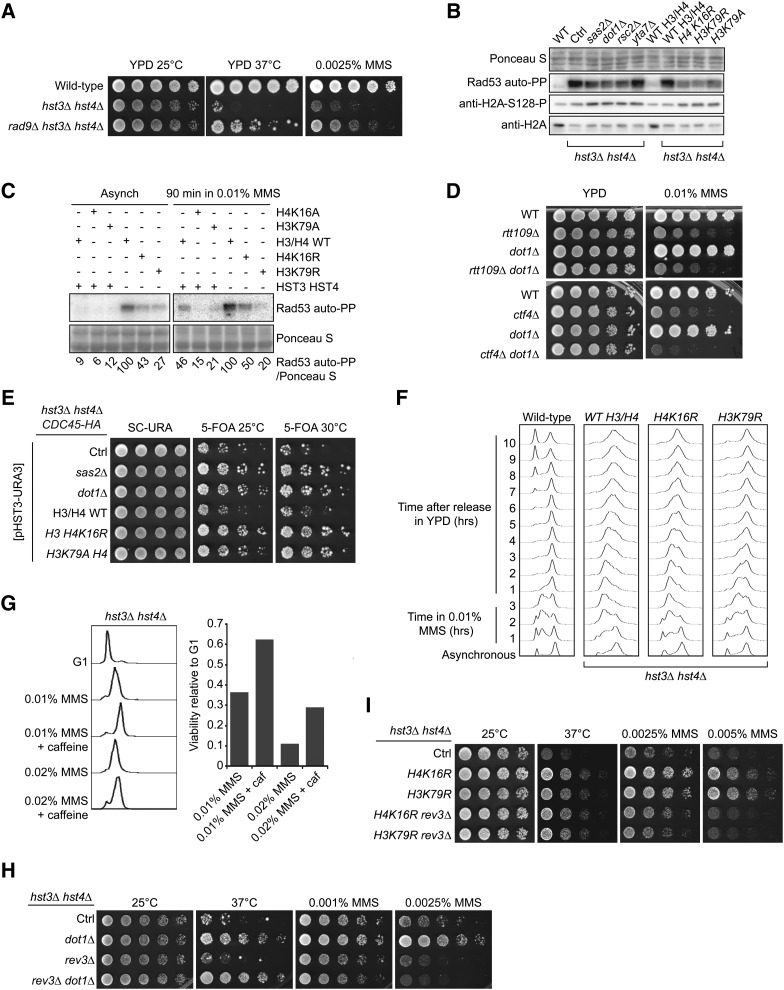
Figure 6.
Mutations that decrease H4K16 acetylation or H3K79 methylation reduce the activity of the DDR kinase Rad53 and suppress the phenotypes of hst3Δ hst4Δ cells. (A) Deletion of RAD9 partially rescues the phenotypes of cells lacking Hst3 and Hst4. Fivefold serial dilutions of cells were spotted onto YPD medium lacking or containing MMS and incubated at 25 or 30°. (B) Suppressor mutations reduce the spontaneous activity of Rad53 in hst3Δ hst4Δ mutants. Whole-cell lysates from cells growing exponentially at 25° were prepared for immunoblotting and Rad53 autophosphorylation assays (see Materials and Methods). (C) Suppressor mutations reduce Rad53 activation in hst3Δ hst4Δ mutants exposed to MMS. Exponentially growing cells of the indicated genotypes were exposed to 0.01% MMS for 90 min. Samples then were prepared for Rad53 autophosphorylation assays. Ponceaus S staining is used as loading control. (D) Deletion of DOT1 does not rescue the MMS sensitivity of rtt109∆ or ctf4∆ mutant cells. Cells were treated as in A except that they were incubated at 30°. (E) The sensitivity of hst3Δ hst4Δ mutants to replicative stress generated by epitope-tagging Cdc45 is rescued by mutations that reduce H3K79Me3 or H4K16Ac levels. Fivefold serial dilutions of cells were spotted onto SC-URA or 5-FOA plates and incubated at 25° or at the semipermissive temperature of 30°. Ctrl: hst3Δ hst4Δ cdc45-HA strain without additional mutation. (F) Exponentially growing cells were incubated in YPD containing 0.01% MMS for 180 min at 25°. Cells were washed with YPD containing 2.5% sodium thiosulfate to inactivate MMS and then incubated in YPD. Samples were collected at the indicated times and processed to determine DNA content by FACS. (G) Cells were arrested in G1 and released into the cell cycle in the presence of the indicated chemicals for 1.5 hr at 25° (right panel). The caffeine concentration was 0.1%. Viability was defined as the ratio of colonies that arose after MMS treatment to colonies formed by G1 cells that were not exposed to MMS. DNA content was analyzed by FACS for each sample (left panel). (H and I) Deletion of REV3 compromises the effect of suppressor mutations on the MMS sensitivity of hst3∆ hst4∆ cells. Fivefold serial dilutions of cells were spotted onto YPD medium lacking or containing MMS and incubated at the indicated temperatures.