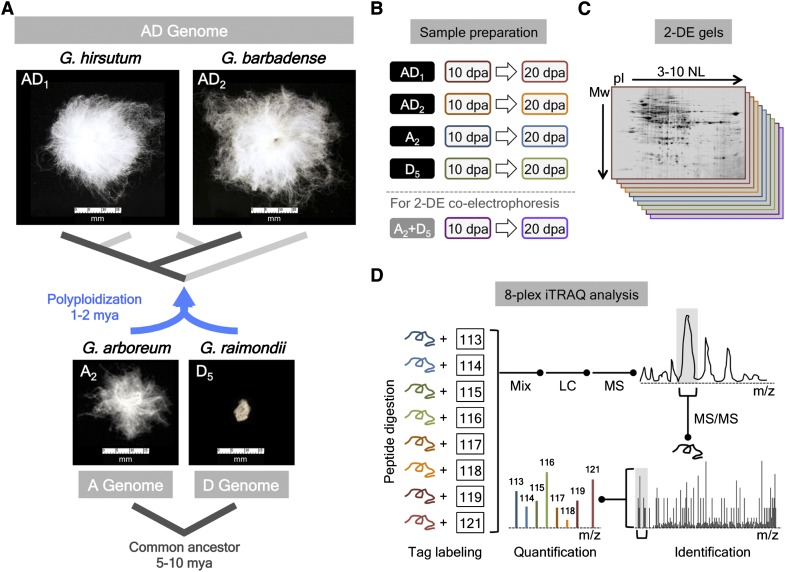
Figure 1.
Comparative proteomics of diploid and allopolyploid cotton fibers. (A) Phylogenetic framework of diploid and allopolyploid Gossypium illustrating the evolutionary history of allopolyploid AD-genome cottons that diversified from a common polyploidization event between the A- and D-genome diploids. A representative image of a single seed with attached fibers is shown for each species. (B) For sample preparation, total proteins were extracted from 10- and 20-dpa fibers in each species for 2-DE and iTRAQ analyses, and in addition, the diploid A- and D-genome protein extracts were mixed to a ratio of 1:1 for coelectrophoresis in 2-DE analysis. (C) The extracted proteins and diploid protein mixtures were separated in 2-DE experiments with a nonlinear IEF range of pH 3–10, and the resulting gels were subjected to image analysis for spot detection and protein quantification based on spot volumes. (D) In iTRAQ analyses, extracted proteins were separately digested and labeled with iTRAQ tags, and the combined peptide mixture was subjected to liquid chromatography (LC) coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (MS) analyses. The iTRAQ reagents allow simultaneous identification and quantitation of proteins in eight different samples.