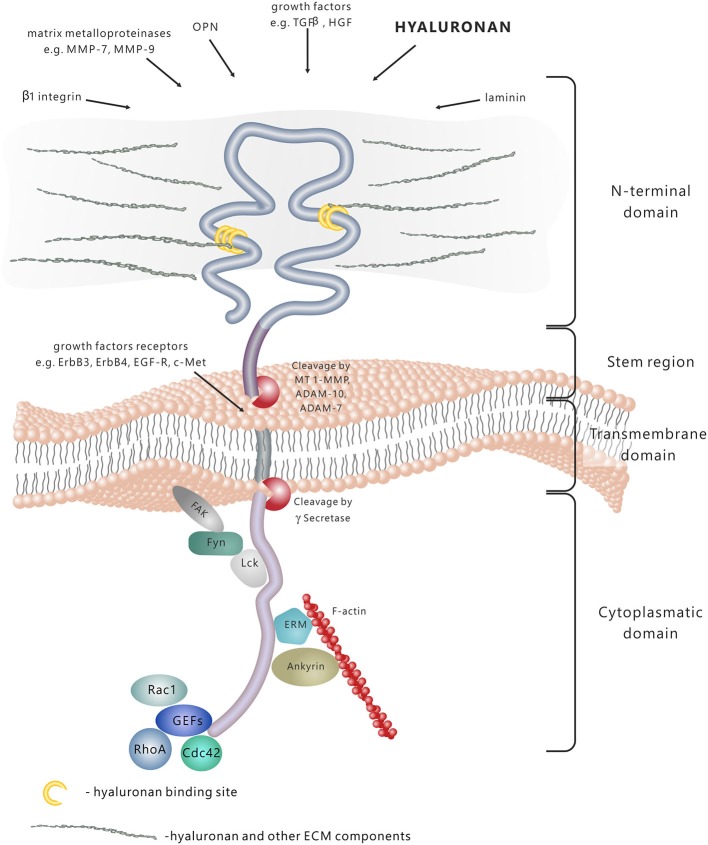
Figure 1.
CD44 protein structure and signaling. CD44 is a transmembrane molecule composed of several domains. The N-terminal extracellular domain can bind various ligands, including hyaluronan (HA), extracellular matrix (ECM) glycoproteins and proteoglycans, growth factors, cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases. In result of the proteolytic cleavage within the stem region, the extracellular domain is released into the extracellular space. The transmembrane domain anchors and stabilises the molecule in the plasma membrane. The cytoplasmic domain is responsible for signal transduction through binding to different molecules, including cytoskeleton components, kinases and activators of small Rho GTPases (GEFs-guanine nucleotide exchange factors).