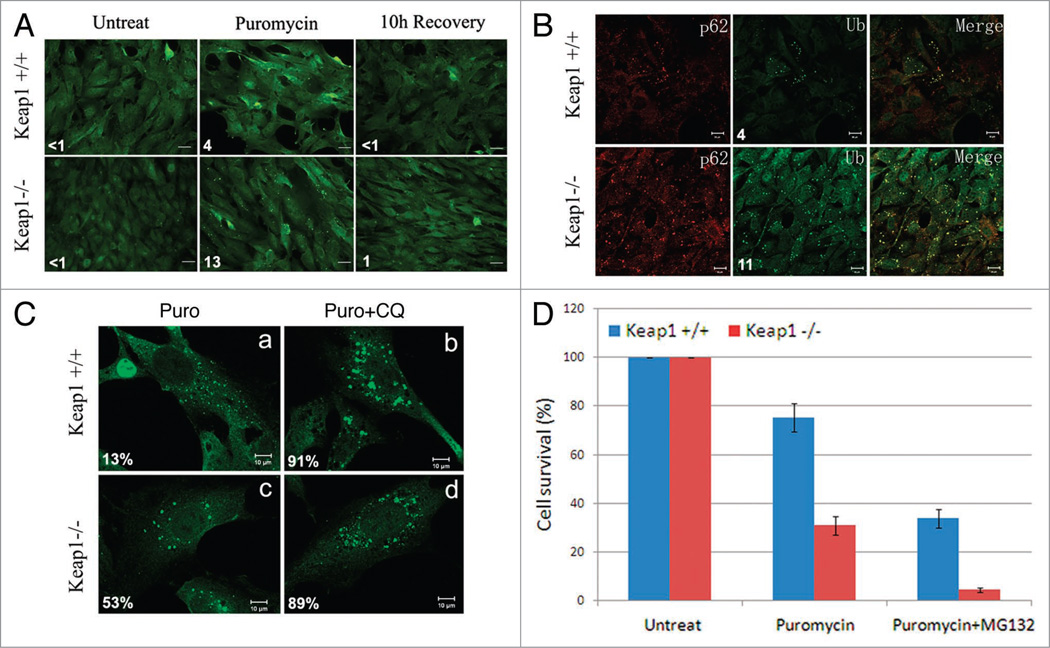
Figure 5.
Keap1 ablation leads to ubiquitin aggregates accumulation and cytotoxicity. (A) Ubiquitin aggregates in Keap1 knockout cells. Keap1+/+ and Keap1−/− MEF cells were treated with 10 µg/ml puromycin for 4 hours, and recovered in normal DMEM for another 10 hours. Cell were then fixed and stained with FK2 antibody. These images are representative of at least three independent experiments. The numbers of ubiquitin puncta per cell were summarized from at least 200 cells in three different experiments. (B) Keap1 wild-type and knockout MEFs were treated with puromycin for 4 hours. p62 and ubiquitin (Ub) were stained by anti-p62 or FK2 antibodies respectively. The numbers of ubiquitin puncta per cell were summarized from at least 200 cells in three different experiments. (C) Keap1+/+ and Keap1−/− cells were either treated with 10 µg/ml puromycin for 4 hours, or with 10 µg/ml puromycin and 200 µM chloroquine for 4 hours. Cells were then fixed and stained with FK2 antibody. These images are representative of at least three independent experiments. The percentage of large aggregates (twice the size of smaller ones) in total aggregates was summarized from at least 200 cells. (D) Keap1 wild-type and knockout cells were mock treated or treated with puromycin (10 µg/ml) alone, or co-treated with puromycin and MG132 (2 µM) for 4 hours. Cell numbers were counted 2 days after treatments in a Trypan blue assay. There data were summarized from three different experiments.