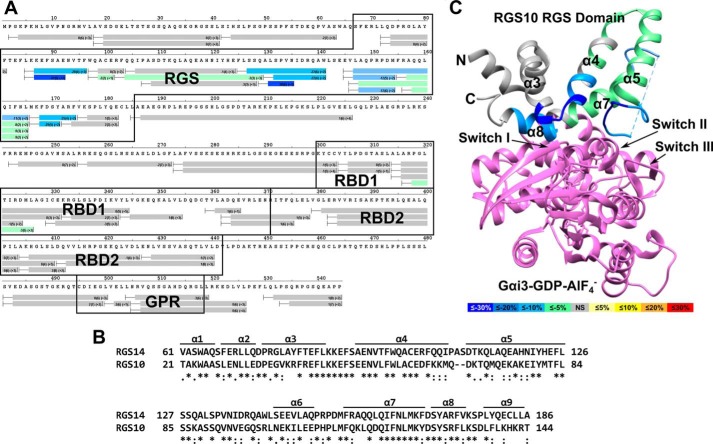
FIGURE 4.
Gαo activated with AlF4− binds and markedly stabilizes the RGS domain of RGS14. A, differential HDX heat map for the RGS14·Gαo-AlF4− complex. Each bar represents an individual peptide with the color corresponding to the average percentage change in deuterium exchange between apo-RGS14 and RGS14·Gαo-AlF4− over six time points (10, 30, 60, 300, 900, and 3,600 s). The numbers in the first parentheses indicate the S.D. for three replicates. The numbers in the second parentheses indicate the charge of the peptide. Residues corresponding to the RGS domain, RBDs, and GPR motif are boxed in black. Changes in deuterium exchange are indicated by the colored scale bar. B, ClustalΩ sequence alignment of rat RGS14 and human RGS10. Asterisks indicate fully conserved residues, colons indicate conservation of strongly similar properties, and periods indicate conservation of weakly similar properties. C, average percentage change in deuterium exchange levels mapped onto the crystal structure of human RGS10 bound to AlF4−-activated Gαi3 (PDB ID: 2IHB). Gαi3 is represented in purple. Differences in the percentage of deuterium exchange are indicated by the colored scale bar.