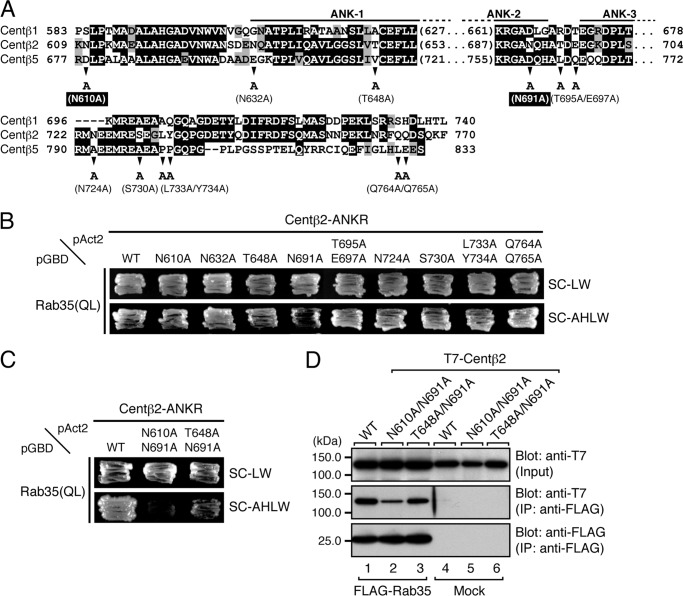
FIGURE 6.
Identification of critical residues responsible for the binding of Rab35 in the ANKR domain of centaurin-β2 by site-directed mutagenesis. A, sequence alignment of the ANKR domains of mouse Centβ1, Centβ2, and Centβ5. Amino acid residues in the sequences that are conserved and that are similar are shown against a black background and a shaded background, respectively. The arrowheads indicate the positions of amino acids that are not conserved between Centβ2 and Centβ1 or Centβ5 and were the focus of the Ala-based site-directed mutagenesis. B, Rab35 binding activity of Centβ2 as determined by yeast two-hybrid assays. Yeast cells containing pAct2 plasmid expressing Centβ2-ANKR(WT) or each Centβ2-ANKR mutant (N610A, N632A, T648A, N691A, T695A/E697A, N724A, S730A, L733A/Y734A, or Q764A/Q765A) and pGBD plasmid expressing Rab35(QL) were streaked on SC-LW (top panel) and SC-AHLW (bottom panel) and incubated at 30 °C. Based on the growth rate of the yeast cells, the N610A, T648A, or N691A mutation in the Centβ2-ANKR appeared to slightly decrease Rab35 binding activity. C, two Asn residues, i.e. Asn-610 and Asn-691, of Centβ2-ANKR are critical for binding Rab35. Yeast two-hybrid assays were performed as described in B. D, the N610A/N691A mutation of Centβ2 dramatically decreased Rab35 binding activity, a finding that was consistent with the results of the yeast two-hybrid assays shown in C. Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed as described in the legend for Fig. 1E. The positions of the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown on the left. IP, immunoprecipitation; ANK1–3, ankyrin repeats 1–3.