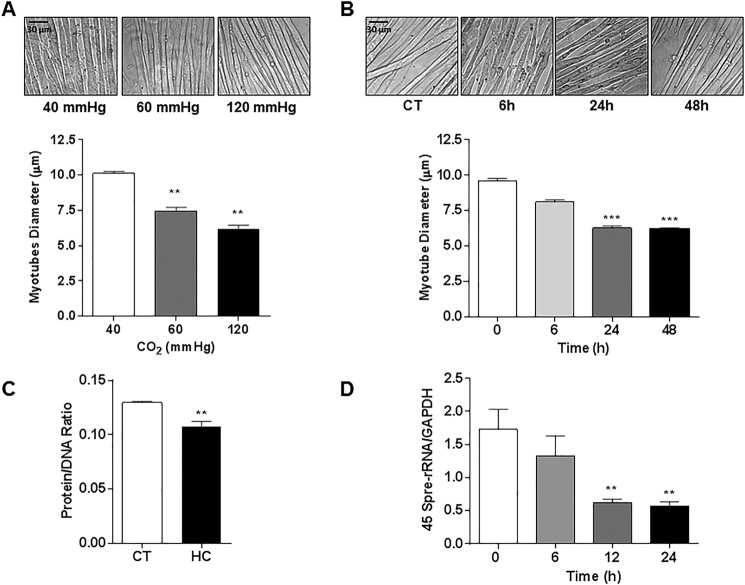
FIGURE 4.
High CO2 exposure causes reduction in myotube diameter associated with a decrease in total protein content and down-regulation of anabolic genes. A, representative images of C2C12 myotubes exposed to 40, 60, and 120 mm Hg CO2, and the graph depicts average myotubes diameter (n = 3). Scale bars, 30 μm. B, representative images of C2C12 myotubes exposed to 0 (CT), 6, 24, and 48 h CO2 (n = 3). C, protein/DNA ratio of C2C12 myotubes exposed to 40 mmHg (CT) or 120 mmHg (HC) for 24 h, as measured with the fluorochrome Hoechst 33258 (n = 3). D, activation of the anabolic 45 S pre-rRNA gene as measured with real time PCR using specific primers (n = 5). **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.