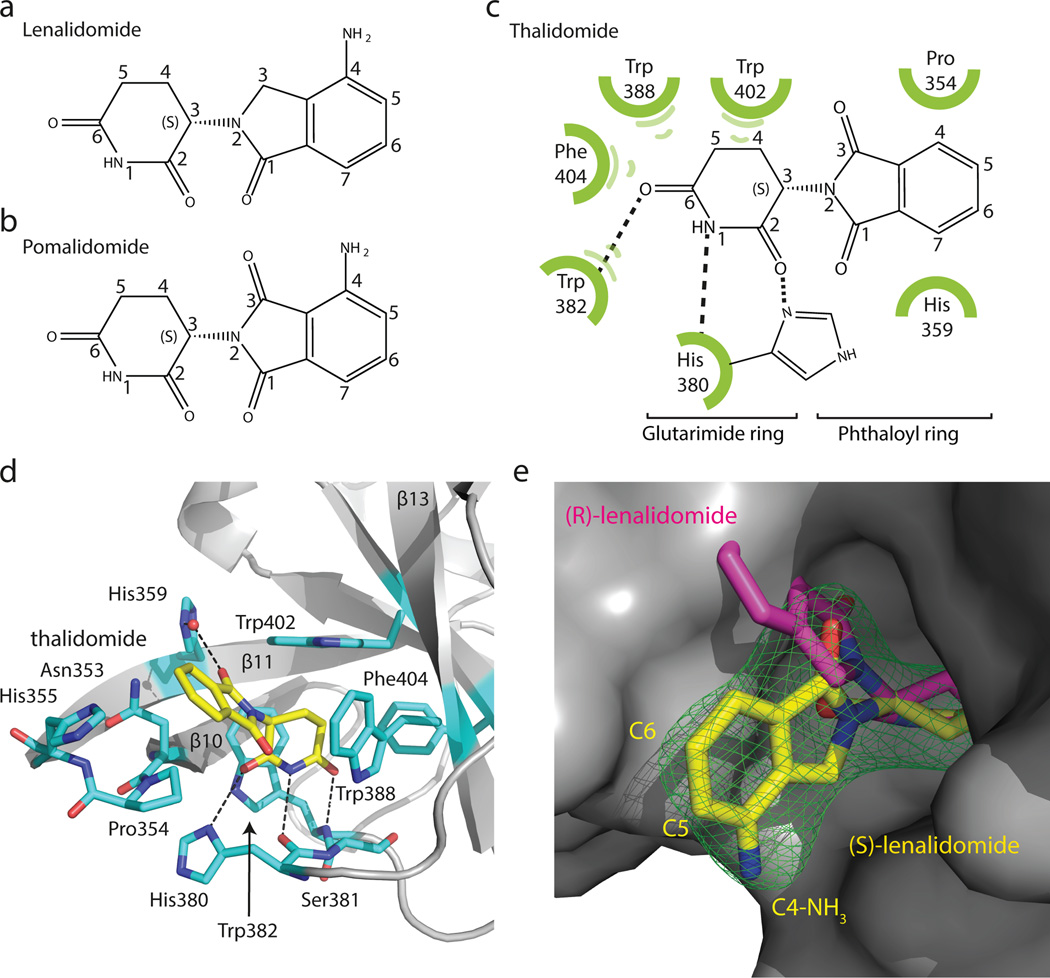
Figure 2. Thalidomide binding to CRBN.
(a) Chemical structure of lenalidomide and (b) pomalidomide. (c) Sketch of thalidomide and its interactions with ggCRBN. (d) IMiDs are anchored through the glutarimide functionality hydrogen-bonding to ggCRBN His380 and Trp382 and the aliphatic face of the glutarimide engulfed in a hydrophobic cage. (e) Surface representation of ggCRBN (grey) and (S)-lenalidomide shown as yellow sticks, together with its positive mFo-DFc electron density (σ=3.5) shown in green. The fit of the (S)- and (R)-enantiomers is indicated.