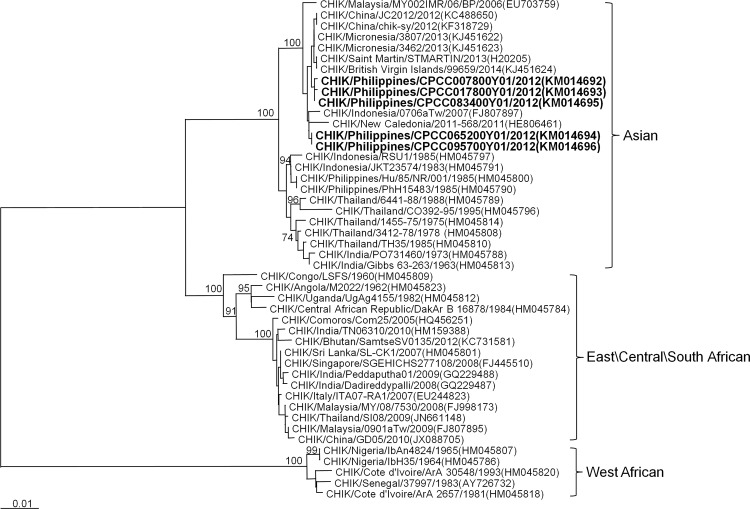
Fig 3. Phylogenetic tree showing five chikungunya viruses (CHIKVs) characterized in the study.
The tree was constructed by neighbor-joining methods (1,000 bootstrap replications) using envelope protein-1 (E1) nucleotide sequences (1,320 bp) of 46 CHIKV strains; the five from the study are designated in bold. Bootstrap support values are shown for major nodes. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. Genotypes are indicated on the right. The sequences were named according to virus/country/strain/year of collection or isolation. GenBank accession numbers are shown in parentheses.