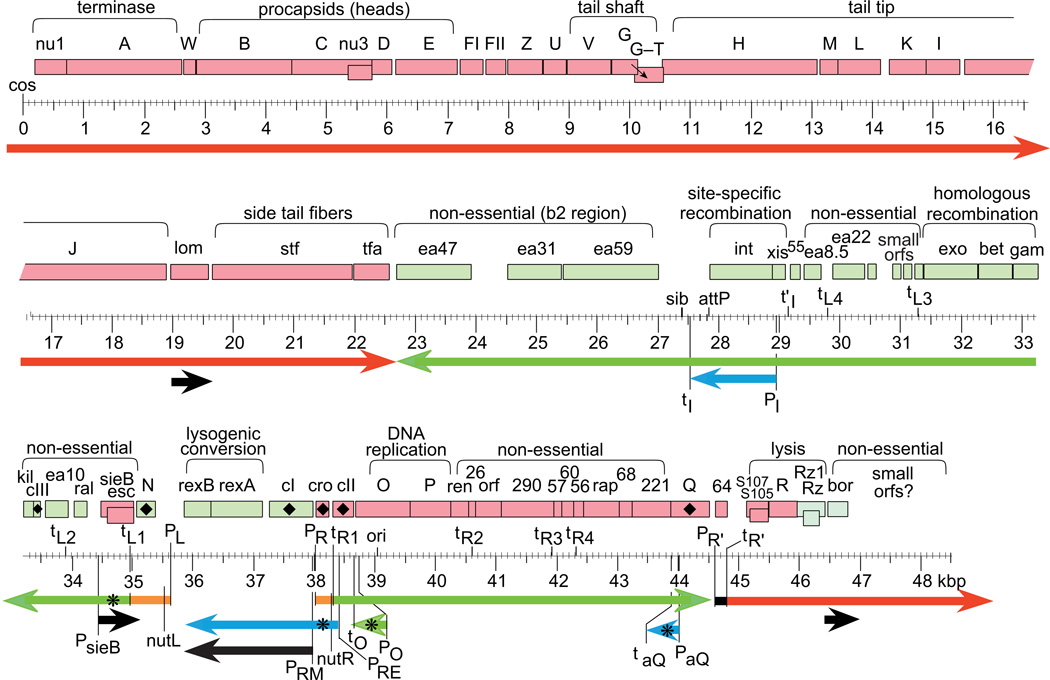
Figure 1. Map of the bacteriophage lambda chromosome.
The linear virion chromosome is shown with a scale in kbp below. Rectangles indicate known genes with names and functional regions shown above; red genes are transcribed rightward and green leftward; vertically offset gene rectangles are expressed from reading frames that overlap (CNu3, S107–S105 and sieB-esc in the same reading frame, rz-rz1 in different frames) or by programmed frameshifting (G-T, small arrow in figure). Diamonds (♦) mark regulatory genes. Important DNA sites (e.g., P, promoters; t, terminators) are indicated below the genes. Thick horizontal arrows below indicate mRNAs: black, transcripts made in a lysogen; orange, immediate-early transcripts; green, early transcripts; red, late transcripts; blue, transcripts made in response to high CII levels. Asterisks (✳) mark RNAs with regulatory activity (the detailed role of PRE-initiated cro antisense message remains unclear (Spiegelman et al., 1972). The chromosome is circularized in the cell during infection, so the PR'-initiated late transcript is continuous from the lower right to the upper left in the figure.