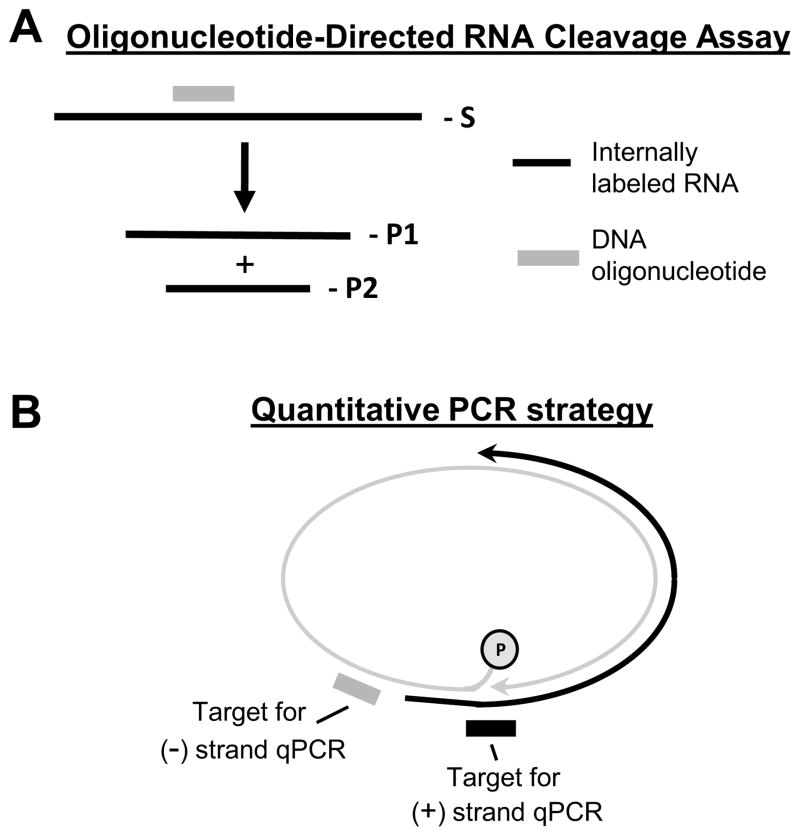
Fig. 2. Principles of the assays to study RNaseH inhibitors.
A. Oligonucleotide-directed RNA cleavage assay to measure RNaseH activity. The substrate (S) is 32P-labeled RNA (black line) annealed to a complimentary DNA oligo (grey line). The RNaseH cleaves the RNA within the RNA/DNA heteroduplex and forms two products (P1 and P2). The reaction products are resolved by denaturing PAGE and detected by autoradiography. B. Basis of the strand-preferential quantitative PCR assay used to measure effects of RNaseH inhibitors on viral replication. The minus-polarity DNA strand (grey line) is detected by amplifying the sequence close to its 5′ end. The plus-polarity DNA strand (black line) is detected by amplifying across the gap in the minus-polarity DNA strand. Modified from (Cai et al., 2014).