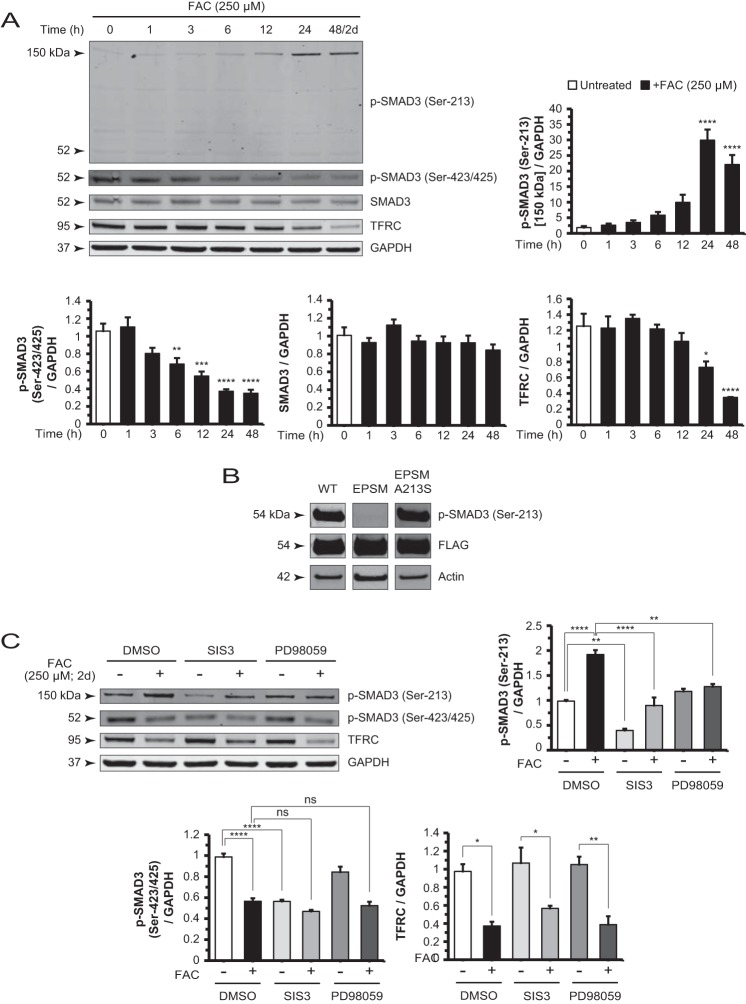
FIGURE 4.
Iron-induced changes in SMAD3 phosphorylation are mediated by non-canonical TGF-β signaling. A, Western blot and densitometry analysis of ARPE-19 cell lysates for p-SMAD3 (Ser-213), p-SMAD3 (Ser-423/425), SMAD3, and TFRC in a FAC treatment time course experiment. The p-SMAD3 (Ser-213) 150-kDa band increased whereas the p-SMAD3 (Ser-423/425) and TFRC bands decreased in intensity in a time-dependent manner. The p-SMAD3 (Ser-213) antibody-detectable 52-kDa band showed no significant change in the same time course. The SMAD3 protein levels also remain unchanged. B, cells transfected with constructs expressing FLAG-tagged SMAD3, SMAD3 EPSM (linker mutations), and SMAD3 EPSM A213S (mutation reverted at residue 213) showed specificity of the antibody used to detect p-SMAD3 (Ser-213) in Western blots. C, Western blot and densitometry analysis of p-SMAD3 (Ser-213) shows that co-treatment with SIS3 or PD98059 and FAC reduced the intensity of this band relative to FAC alone. SIS3 decreased the basal p-SMAD3 (Ser-213) levels. Blotting and analysis of p-SMAD3 (Ser-423/425) demonstrated that SIS3 reduced band intensity to the same extent as FAC alone, whereas PD98059 had no significant effect. Co-treatment with either inhibitor with FAC showed no significant difference from FAC alone. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E. (error bars) (n ≥ 3 with the following statistical notations: *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001; ****, p ≤ 0.0001; ns, not significant).