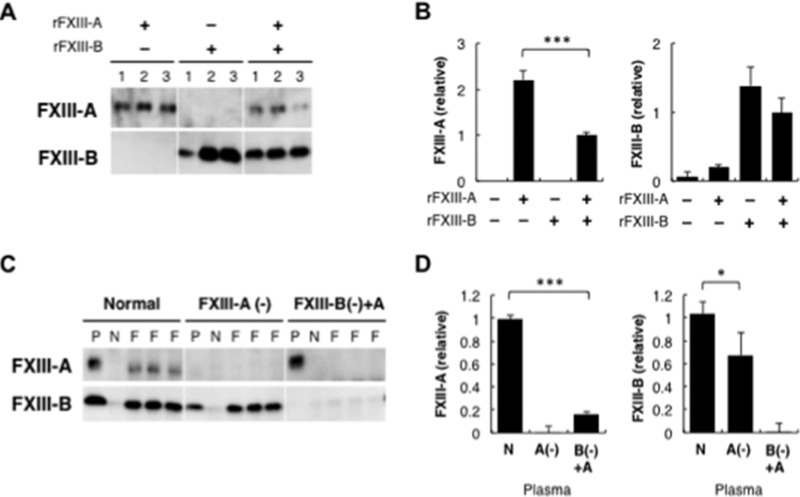
FIGURE 4.
Binding of FXIII to Fbg. A, binding of FXIII to Fbg-Sepharose. rFXIII-A and/or rFXIII-B was reacted with Fbg-Sepharose. The Sepharose of each set of three reactions was analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-FXIII-A antibody (top) or an anti-FXIII-B antibody (bottom). B, ELISA of Fbg-FXIII binding. rFXIII-A and/or rFXIII-B was reacted with Fbg immobilized on a 96-well plate, and ELISA was performed using an anti-FXIII-A antibody (left) or an anti-FXIII-B antibody (right). The mean ± S.D. (error bars) of the amount relative to the reaction with rFXIII-A and rFXIII-B in three reactions is shown. C, co-immunoprecipitation of FXIII with Fbg from plasma. An anti-Fbg antibody (F) or bovine non-immune IgG (N) was added to normal, FXIII-A-depleted, or FXIII-B(−)+A plasma. Immunoprecipitated materials of non-immune IgG and three reactions of anti-Fbg antibody or original plasma (P) were analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-FXIII-A (top) or anti-FXIII-B antibody (bottom). D, ELISA of FXIII bound to Fbg in plasma. Normal (N), FXIII-A-depleted (A(−)), or FXIII-B(−)+rFXIII-A plasma (B(−)+A) was reacted with anti-Fbg antibody immobilized on a 96-well plate, and FXIII-A (left) or FXIII-B (right) bound to the plate was quantitated by ELISA. The mean ± S.D. of the amount relative to normal plasma in three reactions is shown. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001.