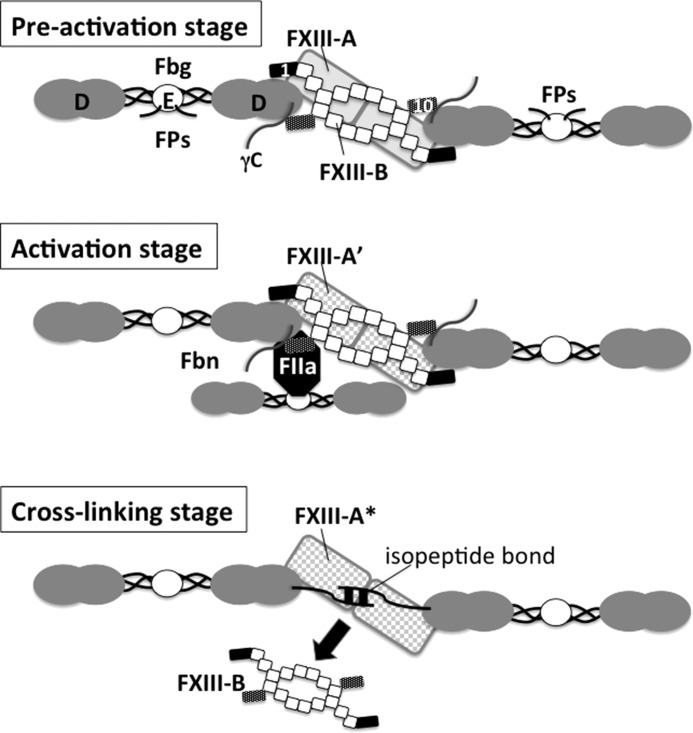
FIGURE 7.
Schematic illustration of possible FXIII-Fbg complex during cross-linking reaction. The FXIII-B dimer is drawn as a series of squares (the second to ninth sushi domains) with two small rectangles (filled rectangle, first sushi domain; dark dotted rectangle, tenth sushi domain). In plasma, the first and tenth sushi domains of a single FXIII-B molecule clip D-domains of two Fbg molecules; thus, these Fbg molecules are connected by FXIII-B (preactivation stage, top). FXIII-A (gray rectangles, the back of FXIII-B) binds to the first sushi domain of FXIII-B. When thrombin (FIIa) is generated to convert Fbg to Fbn by cleaving off fibrinopeptides (Fps) A and B at the amino termini of α and β chains in the Fbg E-domain, thrombin formerly bound to a central E-domain of one Fbn molecule binds to polymerization pocket “a” in a D-domain of another Fbn molecule, allowing thrombin to cleave AP of FXIII-A (activation stage, middle). When FXIII-A* cross-links between C-terminal tails of two Fbn γ-chains, FXIII-B finally dissociates from Fbn (cross-linking stage, bottom). FPs, fibrinopeptides.