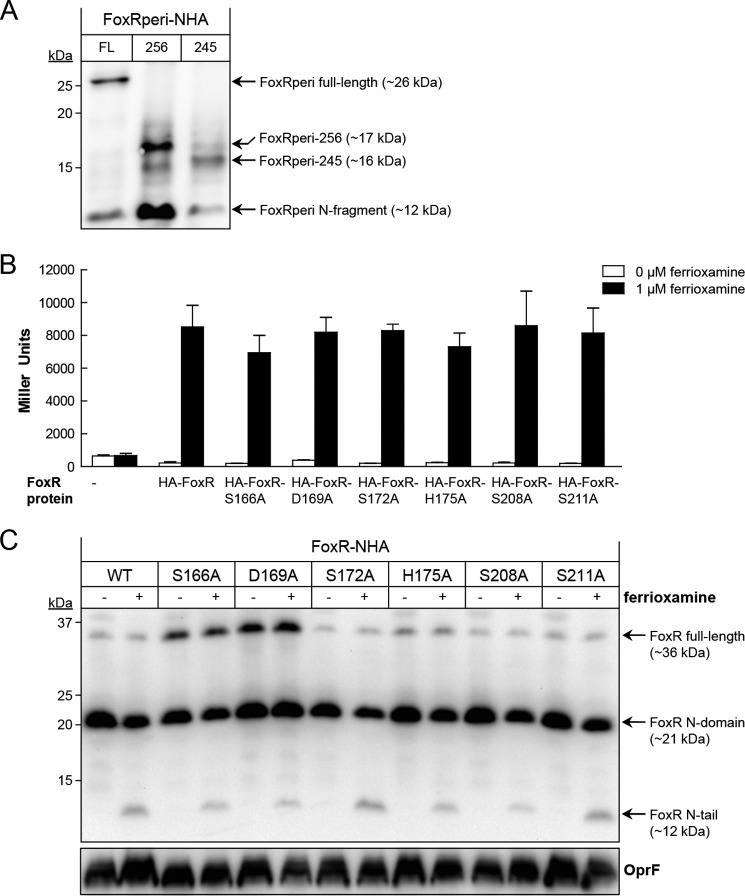
FIGURE 3.
Mutational analysis of putative active site residues of PaFoxR. A, the FoxRperi protein with an N-terminal HA tag (FoxRperi-NHA-FL; amino acids 107–328) was synthesized using the PURExpress® in vitro transcription/translation system. In addition, a FoxRperi-NHA truncate lacking the complete C terminus (FoxRperi-NHA-256; amino acids 107–256) and a truncate also lacking the α-helix (FoxRperi-NHA-245; amino acids 107–245) were produced. Reactions were analyzed by anti-HA immunoblot. B, β-galactosidase activity of the P. aeruginosa PAO1 pvdF ΔfoxR mutant bearing the pMPR8b plasmid (foxA::lacZ transcriptional fusion) and the pMMB67EH (empty), pMMB/HA-FoxR (WT), pMMB/HA-FoxR-S166A, pMMB/HA-FoxR-D169A, pMMB/HA-FoxR-S172A, pMMB/HA-FoxR-H175A, pMMB/HA-FoxR-S208A, or pMMB/HA-FoxR-S211A plasmid expressing the corresponding N-terminally HA-tagged FoxR protein. Bacteria were grown in iron-restricted CAS medium without or with 1 μm ferrioxamine. C, Western blot analysis of the P. aeruginosa pvdF ΔfoxR mutant bearing the pMMB/HA-FoxR (WT) plasmid or one of its derivative plasmids expressing one of the FoxR-S166A, -D169A, -S172A, H175A, or -S211A mutant variants. Bacteria were grown in iron-restricted medium with 1 mm IPTG in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 1 μm ferrioxamine. Proteins were detected using a monoclonal anti-HA tag antibody. As a loading control, a monoclonal antibody against the OprF protein was used. The positions of the molecular size marker (in kDa) and the FoxR protein fragments are indicated.