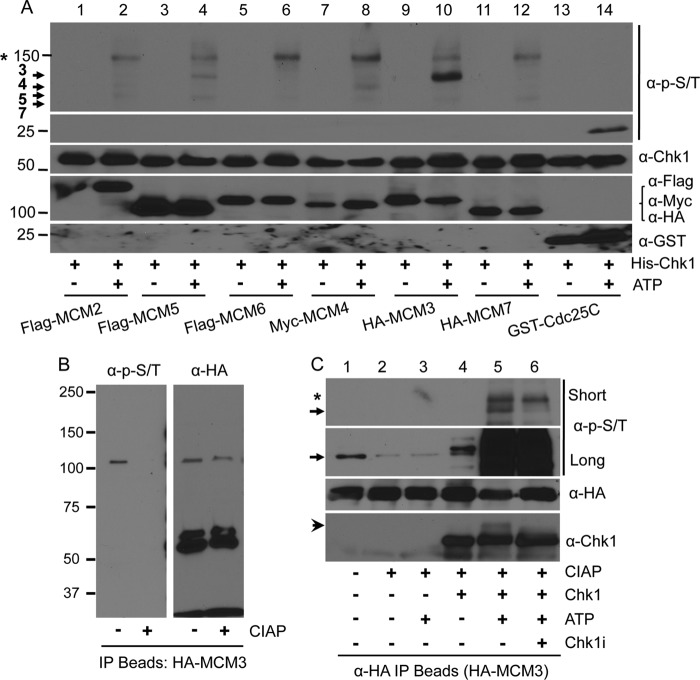
FIGURE 1.
Phosphorylation of MCM3 by Chk1. A, HEK293T cells were transfected with tagged MCM proteins for 48 h, lysed, IPed with antibodies against the tag, and collected on Protein A/G-agarose beads. The beads were treated with 30 units of CIAP at 37 °C for 1 h, and the in vitro kinase assay was performed in the presence or absence of 10 mm ATP with His-Chk1 as the protein kinase. A GST-tagged Cdc25 fragment (200–250) was used as the positive control. The membrane was probed with an antibody mixture at an equal ratio that can recognize potential Chk1 phosphorylation sites. The same membrane was stripped, cut into small sections based on the protein marker, and reblotted with antibodies against Chk1, the tags for MCMs, or GST. Protein markers are shown on the left. Arrows indicate MCM proteins that were phosphorylated. The asterisk indicates a non-MCM protein that was also phosphorylated. B, HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-MCM3, IPed with anti-HA antibodies, treated or not with CIAP, and blotted with the anti-Ser(P)/Thr(P) mixture. The same membrane was stripped and reblotted with anti-HA antibodies. C, an in vitro kinase assay was performed as in A except that the His-Chk1 protein was pretreated with 500 nm Chk1specific inhibitor (Chk1i) for 2 h on ice. Short and long exposures of the ant-Ser(P)/Thr(P) antibody mixture are illustrated to show the difference in the phospho-MCM3 level between cell cultures and in vitro kinase reaction. The arrow denotes HA-MCM3 protein, and the arrowhead in the anti-Chk1 blot indicates autophosphorylated Chk1 proteins. The asterisk indicates the same non-MCM protein as in A.