Figure 1.
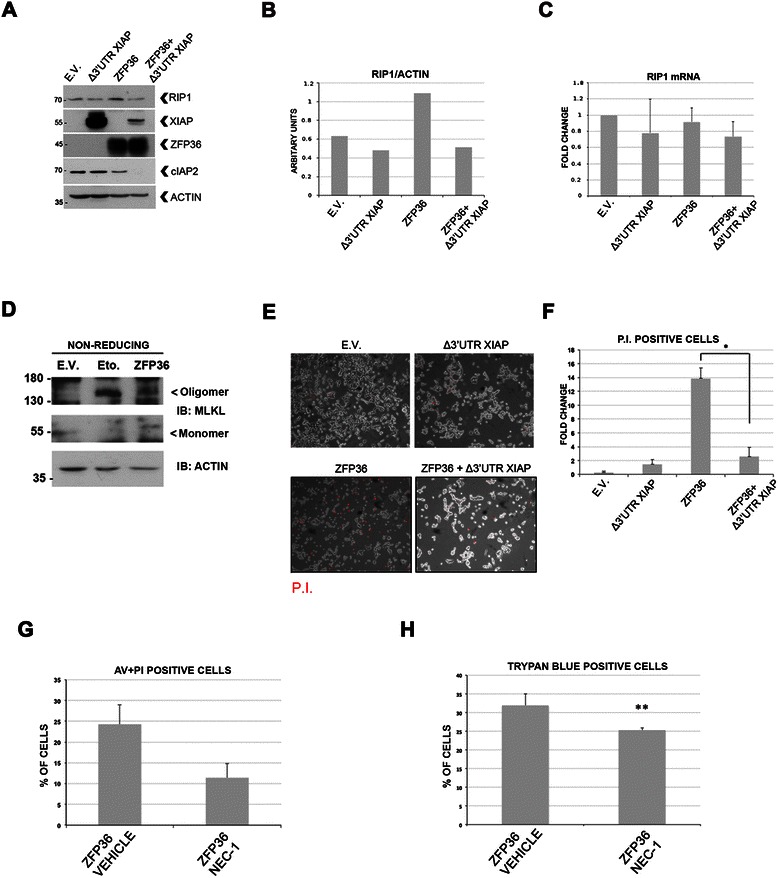
ZFP36 controls RIP1 stability by depleting IAPs and promotes RIP1-dependent cell death. A). Transfection of HEK293T cells with a ZFP36 construct (ZFP36) correlates with the depletion of cIAP2 and with an increase in the stability of RIP1 at 48 hours. HEK293T cells transfected with a XIAP construct depleted of its own 3′UTR (Δ3′UTR XIAP) show a reduction in the levels of RIP1, even in the presence of ZFP36 (ZFP36 + Δ3′UTR XIAP). B) Image J software was used to normalize the levels of RIP1 over beta-ACTIN. C) Real Time PCR showing RIP1 mRNA levels following ZFP36 and Δ3′UTR XIAP over-expression. D) Both the transfection of ZFP36 and the treatment with Etoposide induce the formation of MLKL homo-oligomers and a decrease of MLKL monomers. E.V. cells were incubated with DMSO as this is the vehicle for Nec-1 administration. Non-reducing conditions were applied in order to preserve intact oligomers of MLKL. E) HEK293T transfected with the ZFP36 construct (ZFP36) show increased positivity to Propidium Iodide staining (P.I.), which is reduced in the presence of the Δ3′UTR XIAP construct (ZFP36+ Δ3′UTR XIAP). F) Percentage of P.I. positive cells obtained from 5 fields for each condition from experiment 1C. G-H) 48 hours treatment with 50 μM Necrostatin-1 inhibits ZFP36-dependent cell death (ZFP36 Nec-1) if compared to DMSO treated cells (ZFP36 vehicle), as assessed by cytofluorimetric analysis of Annexin V / P.I. or positivity to Trypan blue. The graphs in this figure represent the mean and SEM calculated on a set of three to four independent experiments (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
