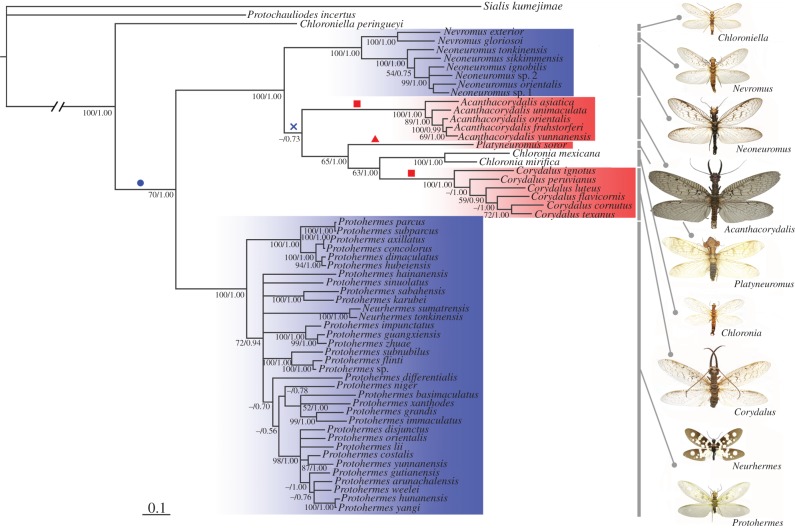
Figure 4.
Phylogeny of 57 dobsonflies (family Corydalidae, subfamily Corydalinae) based on the combined molecular + morphological data inferred from Bayesian analysis. This topology is congruent with the parsimony topology. Bootstrap supports ≥50 and Bayesian posterior probabilities ≥0.50 are given at each corresponding node. Besides Chloroniella, four major lineages are recovered, comprising the Protohermes lineage (Protohermes and Neurhermes), the Neoneuromus lineage (Nevromus and Neoneuromus), the Acanthacorydalis lineage (Acanthacorydalis only) and the Corydalus lineage (Platyneuromus, Chloronia and Corydalus). Lineages marked red exhibit male weapons and lineages marked blue produce large nuptial gifts. Evolutionary gains of large nuptial gifts (blue circle) and male enlarged mandibles (red square) across lineages, as well as secondary loss of large nuptial gifts (blue cross), are shown as supported by ancestral state reconstruction (electronic supplementary material, figure S5). Enlargement in male head flanges (red triangle) is unique to Platyneuromus. The outgroup taxa used here are the fishfly Protochauliodes incertus (family Corydalidae, subfamily Chauliodinae) and the alderfly Sialis kumejimae (family Sialidae) of the same Order Megaloptera.