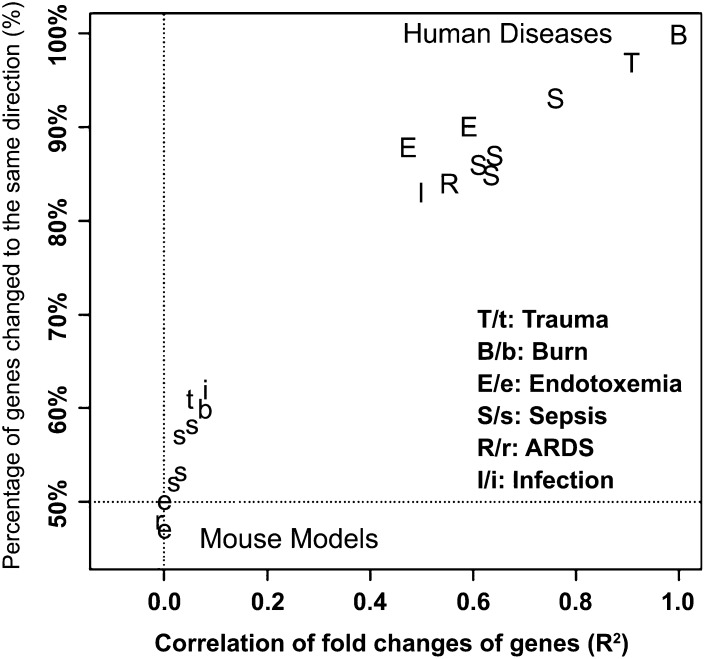
FIGURE 5.
Comparison of the genomic response in circulating leukocytes to severe acute inflammation from 6 distinct causes in human and murine models. GEO was queried for studies in the white blood cells of severe acute inflammatory diseases (i.e., burns, endotoxemia, trauma, sepsis, ARDS, and infection) in humans and mice. The fold-change of each gene measured was calculated between patients and controls in a human study or between treated and control groups in a murine model study; and for a time-course data set, the maximum fold-change was calculated. The gene response in each data set was then compared with the 5554 genes that were significantly changed in human trauma, burns, and endotoxemia. Shown are correlations (x axis) and directionality (y axis) of gene response from the resulting multiple published data sets in GEO compared with human burn injury. ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; GEO, Gene Expression Omnibus. Reproduced from reference 64 with permission.