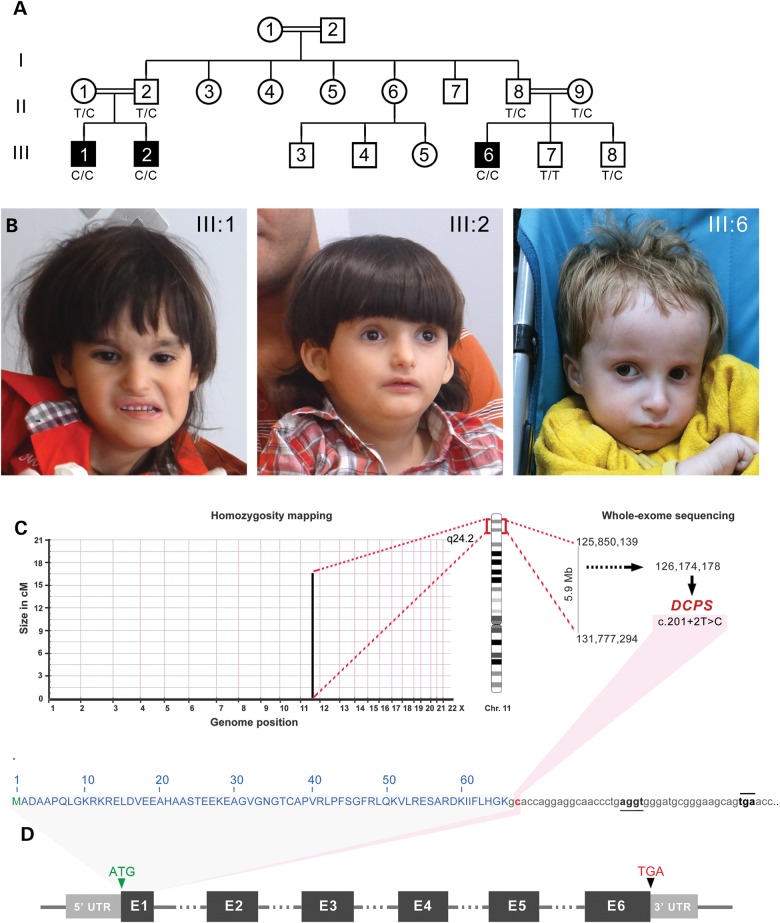
Figure 1.
Phenotypic characteristics of three male propositi with an autosomal recessive Al-Raqad syndrome caused by a splice site mutation in DCPS. (A) Pedigree of Jordanian inbred family with three affected children (III:1, III:2 and III:6) and two unaffected sibs (III:7 and III:8) born to first-cousin parents. (B) Head shot of the three propositi with syndromic craniofacial anomalies, including deep set eyes, thin upper lip, small nose and mild microcephaly. (C) Homozygousity mapping delineates a single candidate region of 5.9 Mb on chromosome 11q. Whole-exome sequencing revealed a private mutation in DCPS in the first splice donor of intron 1: c.201 + 2T > C in the homozygous state. (D) Schematic representation of DCPS exons and location of the mapped mutation in its intron 1 (highlighted in red). Alternative cryptic splice site (underlined) and an in-frame premature termination codon (overlined) are detected 19 and 40 bp downstream of exon 1, respectively.