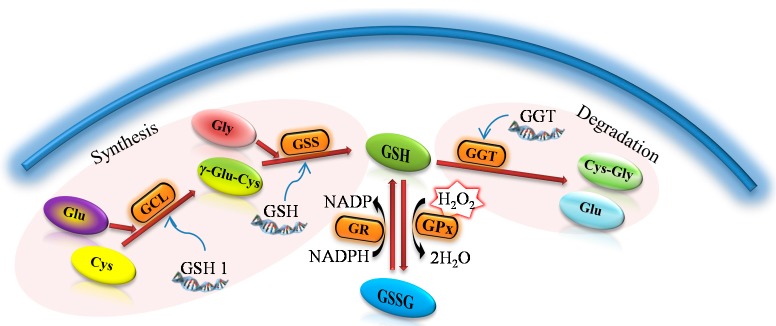
Figure 1.
A general procedure for the synthesis and metabolism of glutathione. γ-glutamylcysteine (γ-Glu-Cys) arises due to the γ-glutamylcysteine synthase (GCL) from glutamic acid (Glu) and cysteine (Cys). The reduced form of glutathion (GSH) is synthesized from GCL and glycine (Gly) due to the glutathione synthase (GSS). As an antioxidant, GSH is oxidized to form oxidized glutathione (GSSG) with the participation of the glutathione peroxidase (GPx). Thanks to the action of glutathione reductase (GR) glutathione occurs primarily in the form of GSH. γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) causes the glutathione degradation in the cells to glutamic acid (Glu) and dipeptide cysteinylglycine (Cys-Gly).