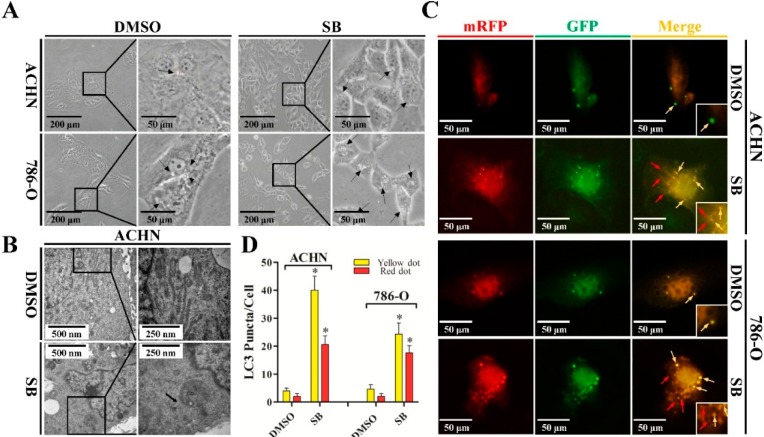
Figure 1.
Silibinin induces autophagic vacuoles in RCC ACHN and 786-O cell lines. (A) Morphological changes of RCC ACHN and 786-O cells after treatment with 50 μM silibinin (SB) as indicated for 24 h by inverted phase contrast microscopy (×40 and ×100). The regions indicated by rectangles are shown with higher magnification. Arrows point to cytoplasmic vacuole accumulation; (B) Representative electron micrographs of cells treated with 50 μM silibinin for 24 h (×20,000 and ×40,000). Arrows point to distinct autophagic structures; (C) Examples of cells transiently transfected with ptfLC3 plasmid and treated with 50 μM silibinin for 24 h under fluorescence microscope (×200). Yellow arrows point to autophagosomes and red arrows point to autolysosomes; and (D) Quantification of the number of autophagosomes (yellow LC3 puncta) and autolysosomes (red LC3 puncta) per cell. Error bars represent SDs. * p < 0.05.