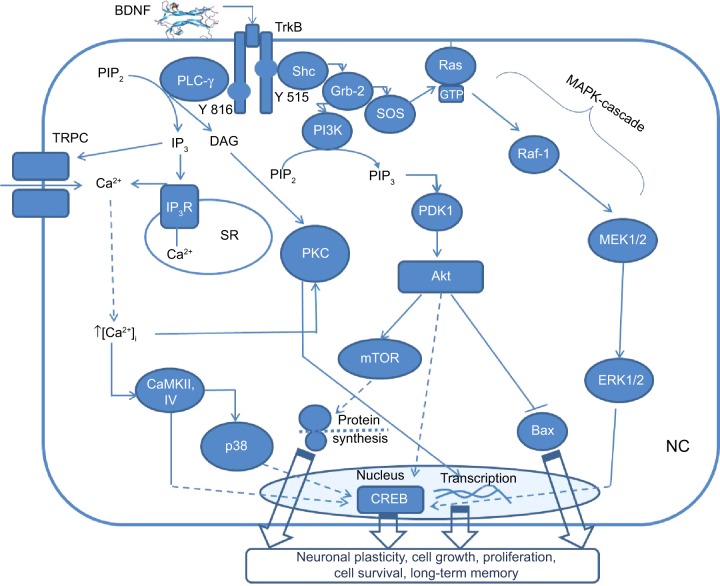
Figure 1.
A general scheme, illustrating BDNF-TrkB signaling through three main pathways in the neuronal cell (NC).
Notes: PLCγ pathway results in activation of neuronal plasticity and long-term memory formation via PKC, TRPC, and transcriptional factor CREB. Also PLCγ activates inositol trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) via IP3 to release intracellular calcium (Ca2+) from sarcoplasmatic reticulum (SR). PI3K-Akt pathway activates CREB and causes further downstream activation of mTOR, which stimulates protein synthesis in neuronal dendrites leading to cell growth, proliferation, and synaptic plasticity. Also, PI3K-Akt pathway blocks Bax protein causing antiapoptotic action. Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) cascade results in activation of transcriptional factor CREB with further stimulation of cell growth, differentiation, protection, releasing of neurotransmitters, and memory formation.
Abbreviations: BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; TrkB, tropomyosin receptor kinase B; PLCγ, phospholipase Cγ; PKC, protein-kinase C; TRPC, transient receptors potential channels; CREB, cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein; Shc, Src-homology 2 domain containing transforming protein; Grb-2, growth factor receptor-binding protein 2; IP3, inositol triphosphate; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; CaMKII, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 2; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKB, protein kinase B; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; Bax, B-cell lymphoma 2 associated X protein; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; SOS, son of sevenless; Ras, rat sarcoma; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; B-Raf, rapid accelerated fibrosarcoma B; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases.