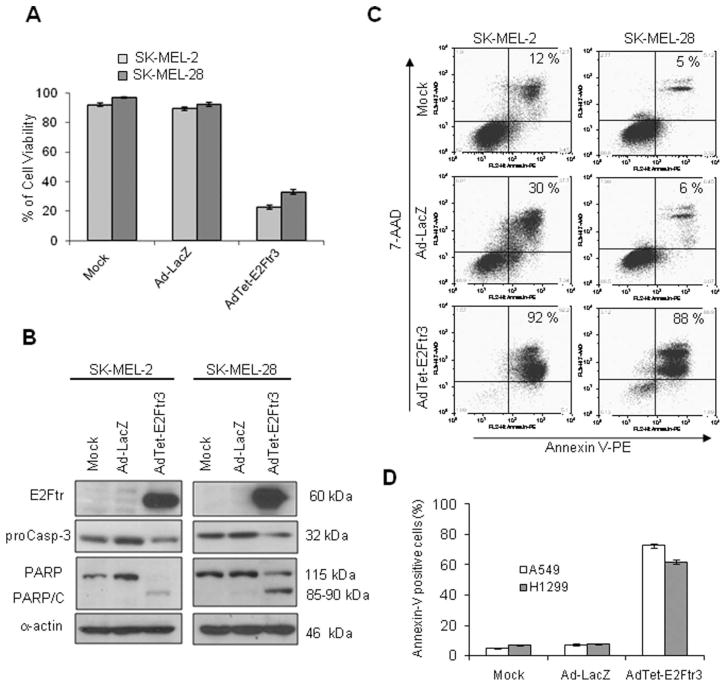
Figure 5.
The role of p53 status on apoptosis induced by the truncated form of the E2F-1 gene (E2Ftr) is illustrated. SK-MEL-2 (mutant p53) cells and SK-MEL-28 (wild type [wt] p53) cells were uninfected (Mock) or were infected with either a recombinant adenovirus (Ad) serotype 5 vector encoding the Escherichia coli β-galactosidase (lacZ) gene controlled by the human cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter (Ad5CMV-LacZ [Ad-LacZ]) or with an Ad vector that expressed E2Ftr under regulation of the tetracycline (Tet)-off system (AdTet-E2Ftr3) at a multiplicity of infection of 100. Seventy-two hours after infection, the cells were used for a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium (MTT) and Western blot analyses or for Annexin V staining. (A) An MTT assay was used to determine cell survival. Each point represents the mean of 3 independent experiments (±standard deviation [bars]). (B) Monoclonal antibody (MoAb) antihuman E2F-1 was used to detect E2Ftr, MoAb antihuman poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) was used to detect PARP, and MoAb antihuman caspase-3/CPP32 was used to detect caspase-3 (proCasp-3). α-Actin was used to demonstrate equal loading for each lane. PARP/C indicates PARP cleavage. (C) For Annexin V-phycoerythrin (PE) staining, cells were stained and analyzed as described in the text (see Materials and Methods). 7-AAD indicates 7-aminoactinomycin D. (D) A549 (wt p53) and H1299 (partial deletion of p53) lung cancer cells were treated as described above and in an apoptosis assay.