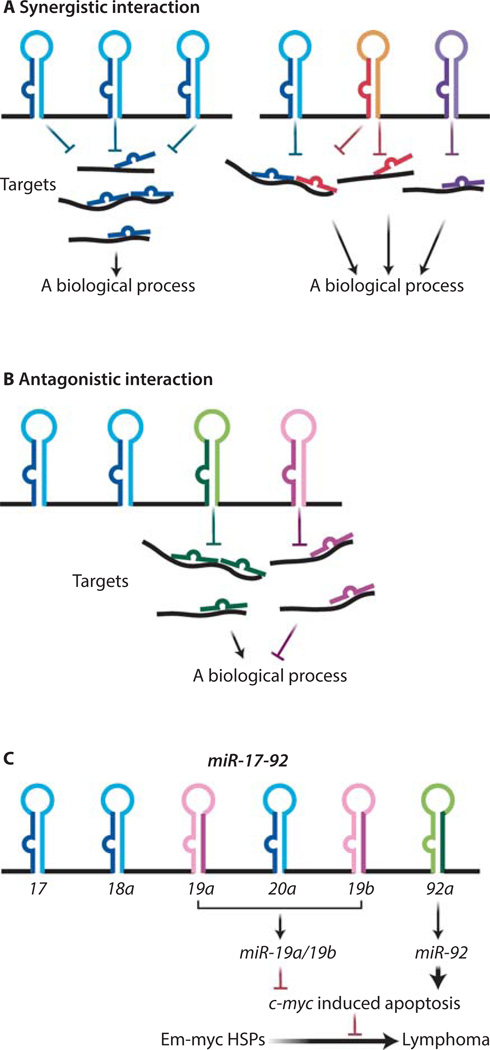
Figure 1. Polycistronic miRNAs harbor complex functional interactions among its components.
(A) Cooperative functional interaction occurs within a polycistronic miRNA. Some polycistronic miRNAs contain a tandem of homologous components that frequently share the same seed sequences, thus they often have the same targets and biological function (right panel). Other miRNA clusters consist of heterologous miRNAs that act on different target sites to synergically regulate one biological process (left panel). (B) miRNA polycistrons can harbor a functional antagonism among the encoded components. (C) A schematic illustration of the miR-19:miR-92 antagonism in regulating the oncogenic cooperation between miR-17–92 and c-Myc. Whereas miR-19 miRNAs repressed c-Myc-induced apoptosis to promote oncogenesis, miR-92 exhibits an opposite effect to promote c-Myc induced apoptosis.