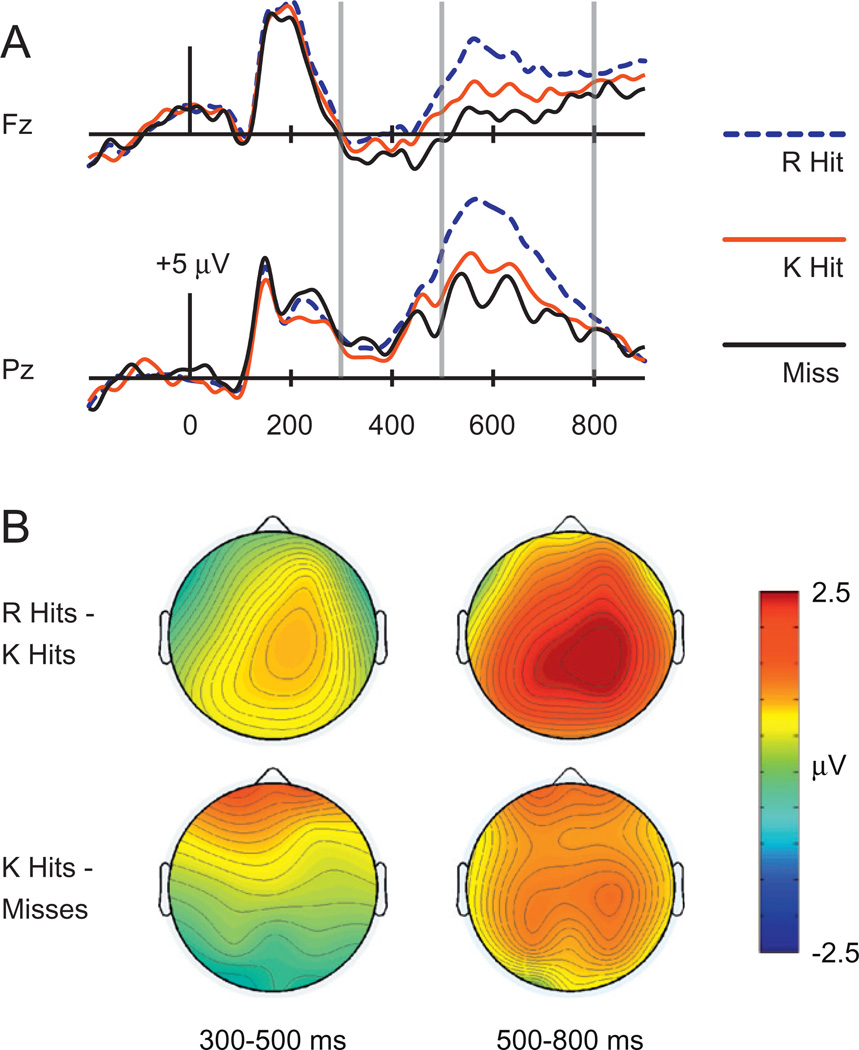
Fig. 1.
ERPs related to recollection (“Remember” hits or R hits), familiarity (“Know” hits or K hits), and misses, collapsed across masked priming conditions in Experiment 1. (A) Waveforms for each condition are shown for midline frontal electrode Fz and midline parietal electrode Pz. Gray vertical lines indicate time windows of interest (300–500 ms and 500–700 ms). (B) Topographical plots depict ERP differences between R hits and K hits (top) and between K hits and Misses (bottom).