FIGURE 3.
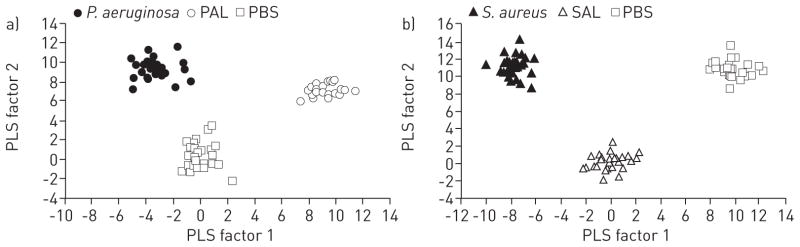
Discriminant analyses using prediction formulae from partial least squares (PLS) regressions for the separation of breathprints from mice with active infections, lysate exposure or untreated controls. a) Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection, P. aeruginosa lysate (PAL) exposure or the untreated PBS controls. The PLS algorithm used nine factors, with a minimum prediction sum of squares (PRESS) residual statistic of 0.45. b) Staphylococcus aureus lung infection, S. aureus lysate (SAL) exposure or the untreated PBS controls. The PLS algorithm used 13 factors, with a minimum PRESS residual statistic of 0.33. The first two PLS factors explain the largest percentage of the variation (P. aeruginosa 28.7%; S. aureus 27.0%) and provide a statistically significant separation of all three groups in each case (p<0.0001). All replicates for all six time points (6, 12, 24, 48, 72 and 120 h) for each group were included, resulting in 88 biological replicates for P. aeruginosa-PAL-PBS (a) and 86 for S. aureus-SAL-PBS (b).
