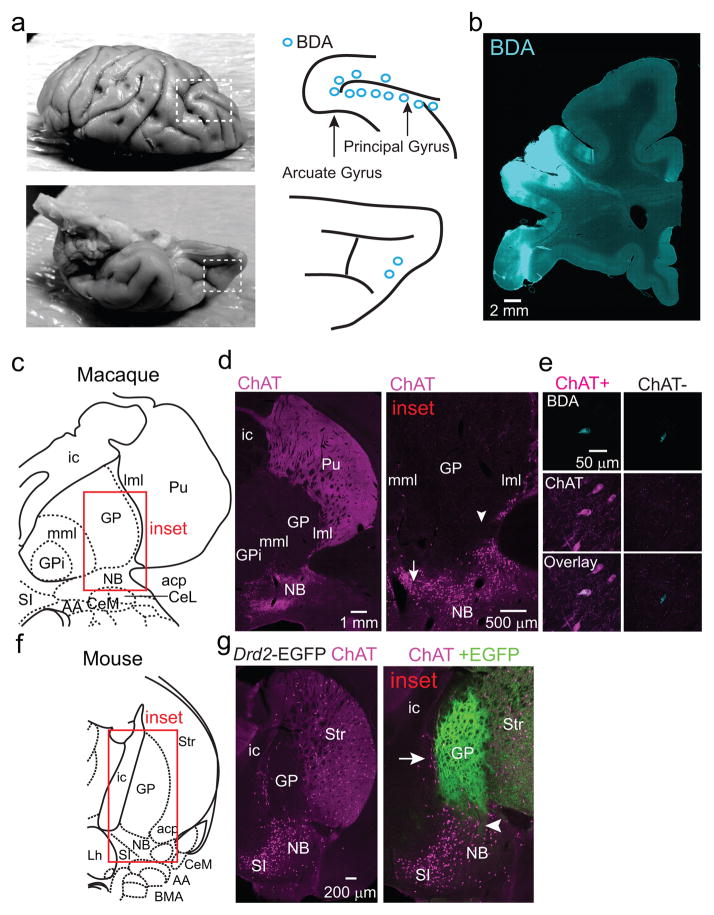
Extended Data Figure 2. ChAT+ and ChAT− GP-FC cells are present in a rhesus macaque.
a. In order to label frontal cortical projection neurons from Ch4iv and Ch4id regions of the NB adjacent to the GP of a rhesus macaque30, the neuronal tracer biotinylated dextran amine (BDA) was injected at multiple sites along the arcuate and principal gyri and in the orbital cortex. Left, dorsal (top) and ventral (bottom) views of a fixed macaque brain. Dashed boxes indicate the injected areas. Right, schematic of the injection sites. Blue circles correspond to 2 x 0.5 μl BDA injections at 1 and 2 mm below the pial surface. b. Coronal section through the injection area after immunostaining to visualize BDA. c–e. Immunostaining for BDA and ChAT identifies retrogradely labeled ChAT+ and ChAT− GP-FC cells. c. Coronal section from macaque atlas containing GP and NB. d. Left, ChAT immunostaining highlights traditional anatomical boundaries of the GP/Putamen and GP/NB. Same plane as in c. Right, higher magnification view of GP/NB border corresponding to the inset in c. ChAT+ neurons are distributed around the ventral GP/dorsal NB and along laminae separating the GP from the Putamen (lateral medullary laminae, lml) and GPi (medial medullary laminae, mml). Arrow and arrowhead indicate approximate locations of BDA+ChAT+ (680 μm anterior) and BDA+ChAT− (360 μm anterior) example GP-FC cells shown in e. e. Single confocal planes showing example BDA+ChAT+ and BDA+ChAT− GP-FC cells. f,g. ChAT immunostaining in a Drd2-EGFP mouse distinguishes traditional anatomical boundaries of the GP/NB from the territory occupied by iSPN axons. f. Coronal section from the mouse atlas. g. Left, ChAT immunostaining highlights traditional anatomical boundaries of the GP/Striatum and GP/NB. Same plane as in f. Right, higher magnification view of GP/NB border region corresponding to the inset in f. As in macaque, ChAT+ cells are distributed along GP borders between striatum and the internal capsule (ic) and at the border of ventral GP/dorsal NB. Overlay of GFP fluorescence demonstrates iSPN axons arborize throughout the GP, abutting ChAT+ cells on the GP border regions (arrow), and ventrally in the dorsal NB (arrowhead). AA, anterior amygdaloid area; ac, anterior commissure posterior; CeL, central lateral division of amygdala; CeM, central medial division of amygdala; GP, globus pallidus externus; GPi, globus pallidus internus; Lh, lateral hypothalamus; Pu, putamen; SI, substantia innominata; Str, striatum.