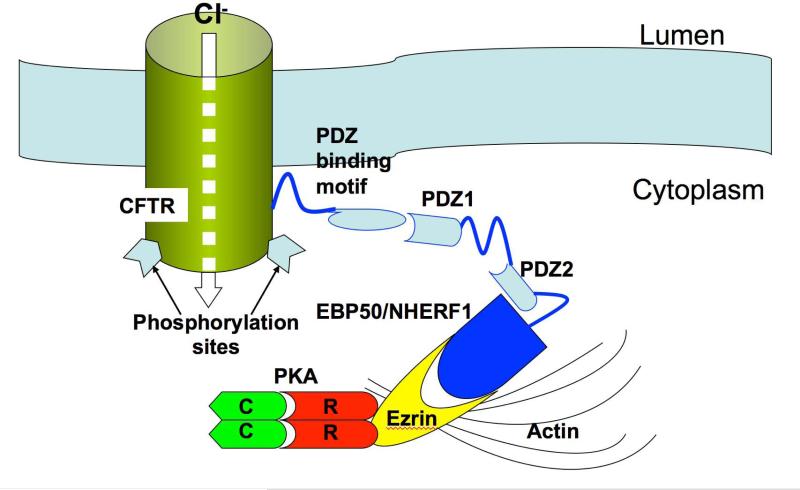
Figure 8.
Schematic depicting possible CFTR-PKA-ezrin interaction at the apical membrane of striated duct cells allowing for rapid and efficient activation of the CFTR channel. PKA is anchored to ezrin via its RII subunits; ezrin in turn binds to EBP50/NHERF1, which has 2 PDZ domains that interact with the PDZ binding motif at the C-terminus of CFTR. Ezrin also binds to actin, which stabilizes the entire complex near the luminal membrane. Not shown are the heterotrimeric Gs protein (48) and other components of signaling pathways demonstrated (in other systems) or presumed to be involved with CFTR localization and activation (β-adrenergic receptor, P2Y2 receptor, adenylate cyclase, protein kinase C, etc.).