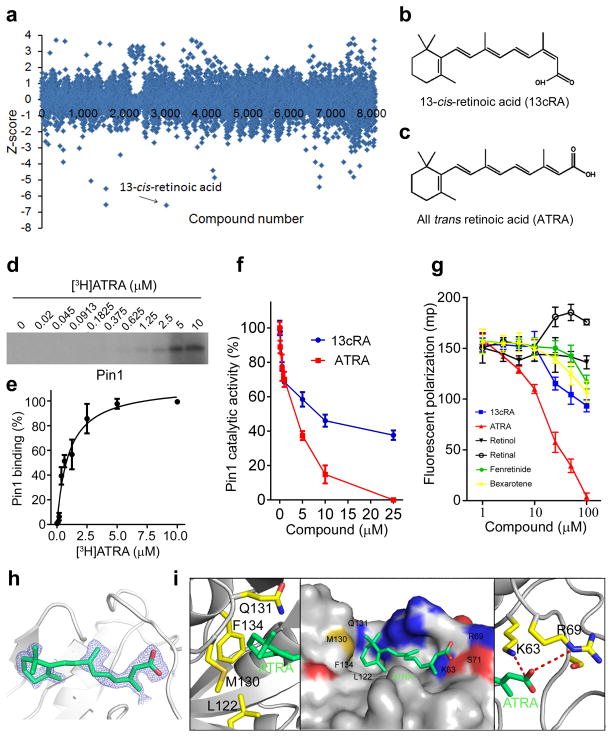
Figure 1. Mechanism-based screening identifies ATRA as a submicromolar Pin1 inhibitor binding to the Pin1 active site.
(a) Summary plot of FP-HTS for Pin1 inhibitors, with 13-cis-retinoic acid having lowest Z score, as determined by folds of standard deviation below the mean of each screening plate.
(b and c) Structures of cis (13cRA) (b) and trans (ATRA) (c) of retinoic acid.
(d and e) [3H]ATRA binding to Pin1 in a dose-dependent manner. Pin1 was incubated with various concentrations of [3H]ATRA, followed by UV exposure before SDS-gel and radiography (d). Pin1-bound [3H]ATRA signals were quantified and plotted against ATRA concentrations (e) (mean ± s.d. of three experiments).
(f) Inhibition of Pin1 catalytic activity by ATRA or 13cRA, as measured by PPIase assay (mean ± s.d. of two experiments).
(g) pTide- HiLyte™ Fluor 488 was added to Pin1, followed by incubation of different concentrations of compounds indicated for 0.5 hour, before FP readout (mean ± s.d. of three experiments).
(h and i) After ATRA soaking, strong electron density was observed at the Pin1 active site in the co-crystal (h). X-ray diffraction of the ATRA-Pin1 co-crystal structure was collected from synchrotron radiation and data were processed and scaled using the HKL2000 software suite (i). ATRA-Pin1 binding (middle) is mediated by salt bridges between the carboxylic acid of ATRA and K63 and R69 residues (right), as well as by hydrophobic interaction between aromatic moiety of ATRA and L122, M130, Q131 and F134 residues (left). The PDB code for the Pin1-ATRA structure is 4TNS.