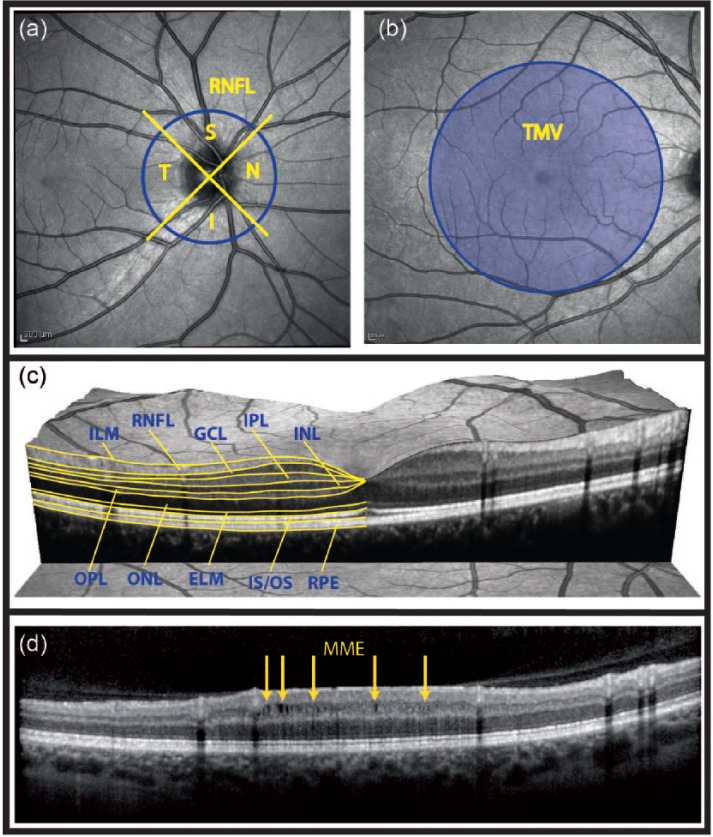
Figure 1.
Retinal parameters acquired by OCT.
(a) Fundus image showing the acquisition of the peripapillary RNFL thickness. OCT records a ring scan of 3.4 mm diameter around the optic nerve head, which is divided into quadrants. (b) The total macular volume is derived from a volume scan and contains all retinal layers in a 6 mm diameter cylinder around the fovea centralis. (c) Intra-retinal layer segmentation in a spectral domain OCT image. (d) MME in a patient with optic neuritis. MME locations are marked by yellow arrows.
OCT: optical coherence tomography; RNFL: retinal nerve fiber layer; S: superior; N: nasal; I: inferior; T: temporal; TMV: total macular volume; GCL; ganglion cell layer; IPL: inner plexiform layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer; ONL: outer nuclear layer; ELM: external limiting membrane; IS/OS: inner segments/outer segments of the photoreceptor layer; RPE: retinal pigment epithelium; MME: microcystic macular edema.