Figure 1.
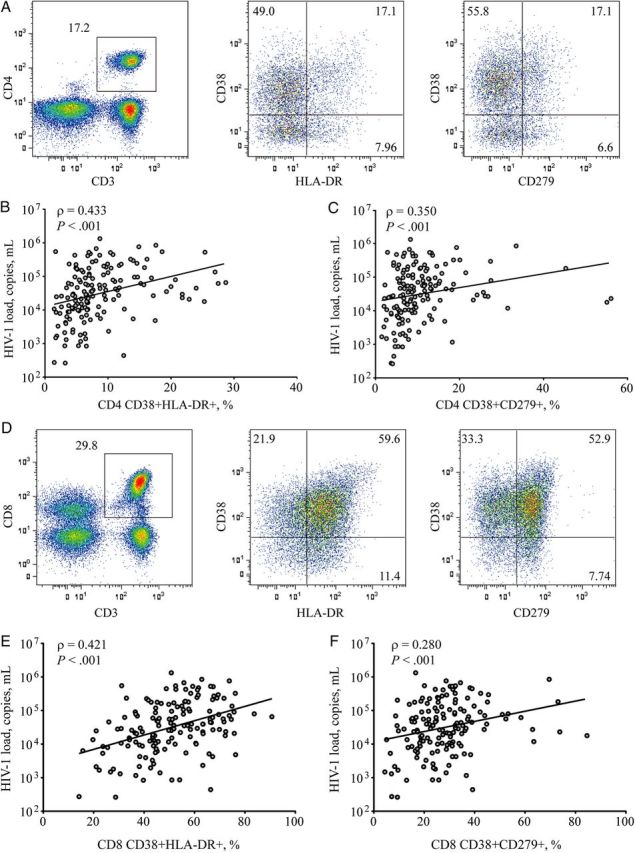
Characterization of immune activation and relationship to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) load. Phenotypic markers of immune activation were enumerated from cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells, using flow cytometry. Lymphocytes were identified on the basis of size and granularity scatter profiles. A, Pseudo-color histogram of CD3-PerCP expression in combination with CD4-FITC identified helper T cells on a representative HIV-infected donor. CD38-PE and HLA-DR-APC, associated with activated phenotypes, or CD38-PE and CD279-APC, corresponding to activated T cells with potentially impaired function, were calculated. B and C, Relationship to HIV-1 load was determined for CD38-PE and HLA-DR-APC (B) and CD38-PE and CD279-APC (C), where positive Spearman correlations were observed. D, Pseudo-color histogram of cytotoxic T cells identified from CD3-PerCP expression in combination with CD8-FITC from a representative HIV-1–infected donor. CD38 and HLA-DR or CD279 in combination were evaluated. E and F, CD38-PE and HLA-DR-APC (E) and CD38-PE and CD279-APC (F) showed a positive relationship to HIV-1 load using a spearman correlation.
