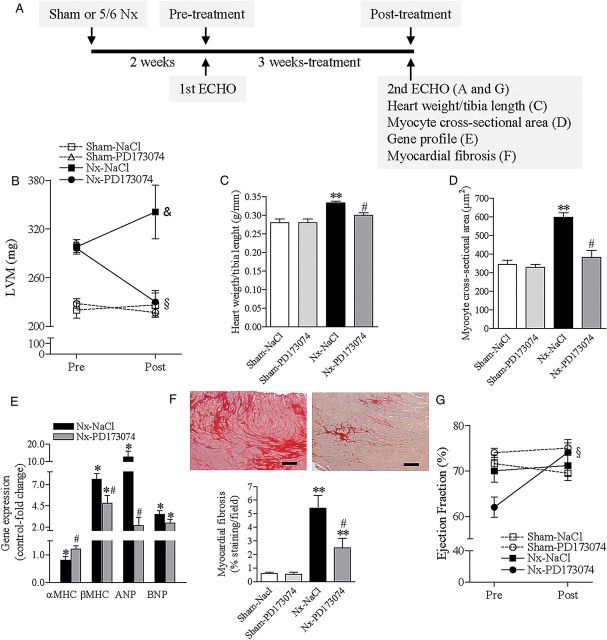
FIGURE 1:
FGFR blockade reverses LVH in an animal model of CKD. (A) Experiment outline. CKD was induced by 5/6 nephrectomy (Nx). After 2 weeks (pre-treatment), LV dimensions and function were determined by echocardiography. Rats were then treated for 3 weeks with vehicle (NaCl 0.9%) or PD173074, 1 mg/kg once-daily. A second echocardiography was repeated at the end of the experiment (3 weeks post-treatment). (B) Echocardiographic measurements of LV mass pre- and post-treatment. (C) At the end of the experiment, LVH was determined as the ratio of heart weight to tibia length. (D) Quantitative analysis of cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area. (E) Expression profile of adult cardiac genes (αMHC), fetal genes (βMHC) and markers of cardiac stress and remodelling (ANP, BNP). Relative gene expression was determined by real-time PCR using gapdh as housekeeping gene. Sham-operated rats were set as control. (F) Representative images of interstitial cardiac fibrosis of 5/6 nephrectomy rats treated with vehicle (left panel) or PD173074 (right panel) for 3 weeks. Staining was performed with Sirius-Red (dark red) (original magnification, ×20; scale bar: 50 µm). The bottom graphic represents quantification of the extent of cardiac fibrosis after 3 weeks of treatment. (G) Echocardiographic measurements of LV ejection fraction pre- and post-treatment. All data are mean ± SEM, n = 8 for Sham–Vehicle, 4 for Sham–PD173074, n = 8 for 5/6 nephrectomy rats receiving vehicle (Nx–Vehicle) and n = 7 for PD173074 (Nx–PD173074). †P < 0.05 for NaCl- and PD173074-treated rats in comparison with Sham–NaCl pre-treatment, §P < 0.05 for PD173074-treated rats in comparison with pre-treatment, &P < 0.05 for NaCl-treated rats in comparison with PD173074 post-treatment, *P < 0.05 in comparison with Sham–NaCl, **P < 0.05 in comparison with Sham–NaCl and Sham–PD173074; and #P < 0.05 in comparison with 5/6 nephrectomy rats receiving NaCl (vehicle).