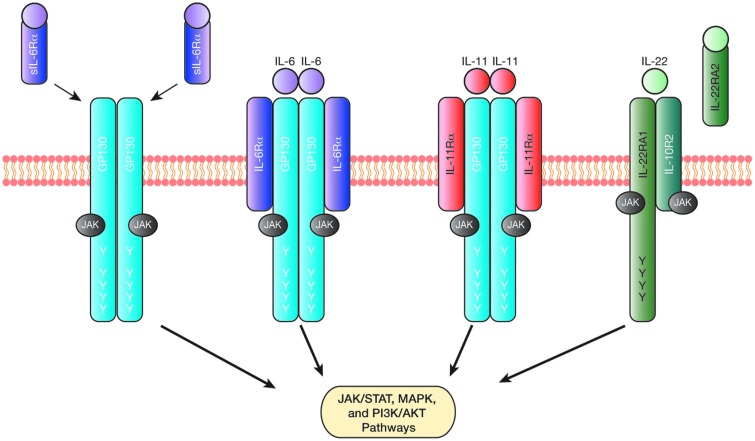
FIG. 1.
Activation of signaling pathways downstream of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-11, and IL-22. IL-6 and IL-11 signal through a hexameric receptor complex consisting of 2 ligands, 2 IL-6Rα or IL-11Rα receptors, and 2 gp130 receptors, while IL-22 signals through a heterodimeric complex comprising one IL-22RA1 and one IL-10R2 receptor. IL-6 can also signal through soluble IL-6Rα (sIL-6Rα) receptors in cells that do not express the transmembrane IL-6Rα receptor, a process referred to as trans-signaling. Meanwhile, IL-22 binding to its soluble receptor, IL-22RA2, prevents ligand-dependent formation of an activated receptor complex. Following receptor engagement, phosphorylation of tyrosine (Y) residues by JAKs allows for subsequent activation of the STAT, MAPK, and PI3K/AKT pathways. The membrane-proximal tyrosine (Y757 in mouse gp130) in gp130 acts as a docking site for the negative regulator SOCS3, and is also required for activation of MAPK signaling.