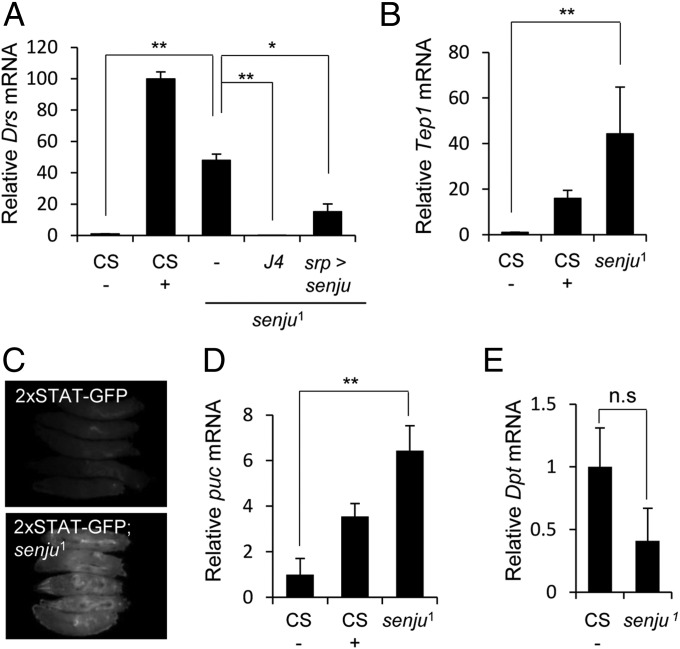
Fig. 2.
Loss of senju induces hyperactivation of the innate immune response. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of Drs expression served as a readout for Toll signaling. Drs expression in challenged (+) and unchallenged (−) WT (CS) larvae [which was set at 1 (control)] and in the unchallenged mutant larvae senju1, senju1 J4, and srp-Gal4 > UAS-senjumyc senju1. (B and D) qRT-PCR analysis of other innate immunity genes, namely Tep1 (used as a readout for the JAK/STAT pathway) (B) and puc (used as a readout for the JNK pathway) (D) in immune-challenged (+) and unchallenged (−) WT larvae (CS) and in the unchallenged mutant larvae, senju1. The values in unchallenged WT were set at 1 (control). (C) senju1;2×STAT-GFP larvae also showed constitutive JAK/STAT pathway activation. (E) qRT-PCR analysis of Dpt (used as a readout for the Imd pathway) in senju1 larvae in the absence of immune challenge. Larvae were challenged with M. luteus (A, B, and D). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (Student t test).