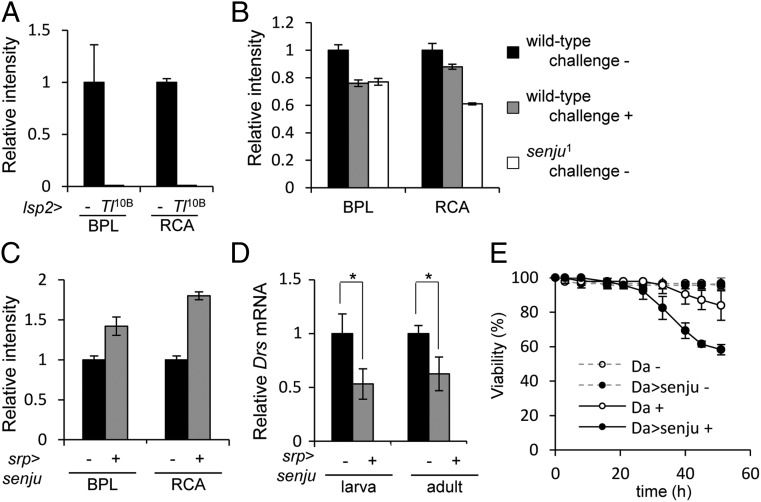
Fig. 5.
Toll activation results in reduced levels of galactose-containing glycans in the hemolymph, which raises the immune response to an adequate level. (A) BPL and RCA120 lectin reactivity of the control (lsp2-Gal4, −) and Toll-activated (lsp2-Gal4 > UAS-Tl10B, Tl10B) hemolymph. (B) BPL and RCA120 lectin reactivity of immune-challenged (with B. subtilis) (+), unchallenged (−) WT, and unchallenged (−) senju1 hemolymph. (C) BPL and RCA120 lectin reactivity of senju-overexpressing (srp-Gal4 > UAS-senjumyc) (+) and control (srp-Gal4, −) hemolymph. (D) Drs expression in immune-challenged (with B. subtilis) larvae and adult flies. (+) indicates senju-overexpressing strains and (–) indicates control srp-Gal4 strains (set at 1). *P < 0.05 (Student t test). (E) Survival of senju-overexpressing (daGal4 > UAS-senjumyc, Da > senju) and control (daGal4>, Da) flies after immune challenge with B. subtilis (+) or no challenge (−).